Natural selection on the Drosophila antimicrobial immune system
- PMID: 18555739
- PMCID: PMC2527063
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2008.05.001
Natural selection on the Drosophila antimicrobial immune system
Abstract
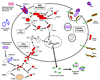
The evolutionary dynamics of immune defenses have long attracted interest because of the special role the immune system plays in mediating the antagonistic interaction between hosts and pathogens. The antimicrobial immune system of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster is genetically well characterized and serves as a valuable model for studying insect and human innate immune defenses. I review here evolutionary and comparative genomic analyses of insect antimicrobial immune genes, with an emphasis on Drosophila. Core signal transduction pathways in the immune system are orthologously conserved across long evolutionary distances, but genes in these pathways evolve rapidly and adaptively at the amino acid sequence level. By contrast, families of genes encoding antimicrobial peptides are remarkably dynamic in genomic duplication and deletion, yet individual genes show little indication of adaptive sequence evolution. Pattern recognition receptors that trigger humoral immunity are evolutionarily rather static, but receptors required for phagocytosis show considerable genomic rearrangement and adaptive sequence divergence. The distinct evolutionary patterns exhibited by these various classes of immune system genes can be logically connected to the functions of the proteins they encode.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamic evolution of the innate immune system in Drosophila.Nat Genet. 2007 Dec;39(12):1461-8. doi: 10.1038/ng.2007.60. Epub 2007 Nov 7. Nat Genet. 2007. PMID: 17987029
-
Relative roles of the cellular and humoral responses in the Drosophila host defense against three gram-positive bacterial infections.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 3;6(3):e14743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014743. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21390224 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive evolution of a novel Drosophila lectin induced by parasitic wasp attack.Mol Biol Evol. 2012 Feb;29(2):565-77. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr191. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Mol Biol Evol. 2012. PMID: 21873297 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila as a model system to unravel the layers of innate immunity to infection.Open Biol. 2012 May;2(5):120075. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120075. Open Biol. 2012. PMID: 22724070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methods for the study of innate immunity in Drosophila melanogaster.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2019 Sep;8(5):e344. doi: 10.1002/wdev.344. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30993906 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolutionary genetics of insect innate immunity.Brief Funct Genomics. 2015 Nov;14(6):407-12. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elv002. Epub 2015 Mar 7. Brief Funct Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25750410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide characterization and expression profiling of immune genes in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.).Sci Rep. 2015 May 6;5:9877. doi: 10.1038/srep09877. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25943446 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of the white body of the squid Euprymna tasmanica with emphasis on immune and hematopoietic gene discovery.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 16;10(3):e0119949. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119949. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25775132 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of a cluster of innate immune genes (beta-defensins) along the ancestral lines of chicken and zebra finch.Immunome Res. 2010 Apr 1;6:3. doi: 10.1186/1745-7580-6-3. Immunome Res. 2010. PMID: 20359324 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immune responses of Drosophila melanogaster are altered by spaceflight.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 11;6(1):e15361. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015361. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21264297 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

