Systemic endocrine instigation of indolent tumor growth requires osteopontin
- PMID: 18555776
- PMCID: PMC4121664
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.04.045
Systemic endocrine instigation of indolent tumor growth requires osteopontin
Abstract
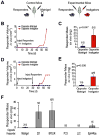
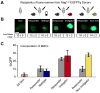
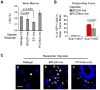
The effects of primary tumors on the host systemic environment and resulting contributions of the host to tumor growth are poorly understood. Here, we find that human breast carcinomas instigate the growth of otherwise-indolent tumor cells, micrometastases, and human tumor surgical specimens located at distant anatomical sites. This systemic instigation is accompanied by incorporation of bone-marrow cells (BMCs) into the stroma of the distant, once-indolent tumors. We find that BMCs of hosts bearing instigating tumors are functionally activated prior to their mobilization; hence, when coinjected with indolent cells, these activated BMCs mimic the systemic effects imparted by instigating tumors. Secretion of osteopontin by instigating tumors is necessary for BMC activation and the subsequent outgrowth of the distant otherwise-indolent tumors. These results reveal that outgrowth of indolent tumors can be governed on a systemic level by endocrine factors released by certain instigating tumors, and hold important experimental and therapeutic implications.
Figures
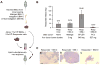
References
-
- Cook AC, Tuck AB, McCarthy S, Turner JG, Irby RB, Bloom GC, Yeatman TJ, Chambers AF. Osteopontin induces multiple changes in gene expression that reflect the six “hallmarks of cancer” in a model of breast cancer progression. Mol Carcinog. 2005;43:225–236. - PubMed
-
- Direkze NC, Alison MR. Bone marrow and tumour stroma: an intimate relationship. Hematol Oncol. 2006;24:189–195. - PubMed
-
- Feng F, Rittling SR. Mammary tumor development in MMTV-c-myc/MMTV-v-Ha-ras transgenic mice is unaffected by osteopontin deficiency. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2000;63:71–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

