Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry determination of plasma 24S-hydroxycholesterol with chromatographic separation of 25-hydroxycholesterol
- PMID: 18555788
- PMCID: PMC2562163
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2008.05.037
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry determination of plasma 24S-hydroxycholesterol with chromatographic separation of 25-hydroxycholesterol
Abstract
Concentrations of circulating 24S-hydroxycholesterol (24SOHChol) are of interest as a practical measure of cholesterol efflux from the human brain. The current method of choice for 24SOHChol quantification is with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) methods to detect 24SOHChol have been described, but they lack rigorous high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) separation of a closely eluting isomeric oxysterol, 25-hydroxycholesterol. This is important because 25-hydroxycholesterol can be present in significant amounts and tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) cannot completely differentiate 24SOHChol. We describe an LC-MS method with rapid chromatographic separation of the oxysterols to permit accurate determination of plasma 24SOHChol. The availability of an LC-MS method offers advantages such as simplified sample work-up and analysis.
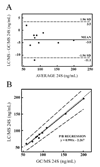
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fast LC-MS/MS analysis of free oxysterols derived from reactive oxygen species in human plasma and carotid plaque.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Oct 21;425:3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.06.022. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23827692
-
Method development for the determination of 24S-hydroxycholesterol in human plasma without derivatization by high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry in atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mode.J Sep Sci. 2015 Oct;38(20):3516-24. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201500719. Epub 2015 Sep 10. J Sep Sci. 2015. PMID: 26249017
-
Determination of 24S- and 27-hydroxycholesterol in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.J Lipid Res. 2004 Apr;45(4):776-81. doi: 10.1194/jlr.D300036-JLR200. Epub 2004 Jan 16. J Lipid Res. 2004. PMID: 14729854
-
[Current advances in the analysis of free RNA modified nucleosides by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry].Se Pu. 2025 Jan;43(1):3-12. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2024.07004. Se Pu. 2025. PMID: 39722616 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Capillary liquid chromatography combined with tandem mass spectrometry for the study of neurosteroids and oxysterols in brain.Neurochem Int. 2008 Mar-Apr;52(4-5):506-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2007.07.009. Epub 2007 Jul 14. Neurochem Int. 2008. PMID: 17850923 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive method for extraction and quantitative analysis of sterols and secosteroids from human plasma.J Lipid Res. 2012 Jul;53(7):1399-409. doi: 10.1194/jlr.D022285. Epub 2012 Apr 19. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22517925 Free PMC article.
-
Liver x receptor modulation of gene expression leading to proluteolytic effects in primate luteal cells.Biol Reprod. 2012 Mar 30;86(3):89. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.111.096347. Print 2012 Mar. Biol Reprod. 2012. PMID: 22156476 Free PMC article.
-
Brain cholesterol metabolism, oxysterols, and dementia.J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;33(4):891-911. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-121585. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013. PMID: 23076077 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometry techniques in the survey of steroid metabolites as potential disease biomarkers: a review.Metabolism. 2013 Sep;62(9):1206-17. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.04.003. Epub 2013 May 7. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 23664145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydroxycholesterol Levels in the Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Neuromyelitis Optica Revealed by LC-Ag+CIS/MS/MS and LC-ESI/MS/MS with Picolinic Derivatization: Increased Levels and Association with Disability during Acute Attack.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 12;11(12):e0167819. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167819. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27942009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Björkhem I, Meaney S. Brain cholesterol: long secret life behind a barrier. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004;24:806–815. - PubMed
-
- Lütjohann D. Cholesterol metabolism in the brain: importance of 24S-hydroxylation. Acta. Neurol. Scand. Suppl. 2006;185:33–42. - PubMed
-
- Björkhem I, Lütjohann D, Diczfalusy U, Stahle L, Ahlborg G, Wahren J. Cholesterol homeostasis in human brain: turnover of 24S-hydroxycholesterol and evidence for a cerebral origin of most of this oxysterol in the circulation. J. Lipid Res. 1998;39:1594–1600. - PubMed
-
- Björkhem I. Rediscovery of cerebrosterol. Lipids. 2007;42:5–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

