White matter changes contribute to corpus callosum atrophy in the elderly: the LADIS study
- PMID: 18556357
- PMCID: PMC8119069
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A1169
White matter changes contribute to corpus callosum atrophy in the elderly: the LADIS study
Abstract
Background and purpose: The corpus callosum (CC) is the most important structure involved in the transmission of interhemispheric information. The aim of this study was to investigate the potential correlation between regional age-related white matter changes (ARWMC) and atrophy of CC in elderly subjects.
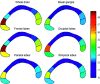
Materials and methods: In 578 subjects with ARWMC from the Leukoaraiosis And DISability (LADIS) study, the cross-sectional area of the CC was automatically segmented on the normalized midsagittal MR imaging section and subdivided into 5 regions. The ARWMC volumes were measured quantitatively by using a semiautomated technique and segmented into 6 brain regions.
Results: Significant correlation between the area of the rostrum and splenium regions of the CC and the ARWMC load in most brain regions was identified. This correlation persisted after correction for global atrophy.
Conclusion: Increasing loads of ARWMC volume were significantly correlated with atrophy of the CC and its subregions in nondisabled elderly subjects with leukoaraiosis. However, the pattern of correlation between CC subregions and ARWMC was not specifically related to the topographic location of ARWMC. The results suggest that ARWMC may lead to a gradual loss of CC tissue.
Figures



References
-
- Hampel H, Teipel SJ, Alexander GE, et al. Corpus callosum atrophy is a possible indicator of region- and cell type-specific neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer disease: a magnetic resonance imaging analysis. Arch Neurol 1998;55:193–98 - PubMed
-
- Moretti M, Carlucci G, Di CA, et al. Corpus callosum atrophy is associated with gait disorders in patients with leukoaraiosis. Neurol Sci 2005;26:61–66 - PubMed
-
- Lyoo IK, Satlin A, Lee CK, et al. Regional atrophy of the corpus callosum in subjects with Alzheimer's disease and multi-infarct dementia. Psychiatry Res 1997;74:63–72 - PubMed
-
- Ryberg C, Rostrup E, Stegmann MB, et al. Clinical significance of corpus callosum atrophy in a mixed elderly population. Neurobiol Aging 2007;28:955–63 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
