ID1, inhibitor of differentiation/DNA binding, is an effector of the p53-dependent DNA damage response pathway
- PMID: 18556654
- PMCID: PMC2504896
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M800643200
ID1, inhibitor of differentiation/DNA binding, is an effector of the p53-dependent DNA damage response pathway
Abstract
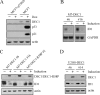
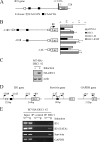
ID1, inhibitor of differentiation/DNA binding, plays an important role in cell proliferation, differentiation, and tumorigenesis. It has been shown that ID1 is de-regulated in multiple cancers and up-regulation of ID1 is correlated with high grades and poor prognosis of human cancers. In contrast, the p53 tumor suppressor was found to be mutated or inactivated in most human cancers and loss of p53 results in early onset of multiple cancers. Although the biological functions of the ID1 oncogene and the p53 tumor suppressor have been intensively investigated, little is known about the upstream regulators of ID1 and the cross-talk between ID1 and p53. Here, we showed that ID1 is down-regulated in cells treated with various DNA damage agents in a p53-dependent manner. Interestingly, we found that DEC1, which was recently identified as a p53 target and mediates p53-dependent cell cycle arrest and senescence, is capable of inhibiting ID1 expression. Conversely, we found that knockdown of DEC1 attenuates DNA damage-induced ID1 repression. In addition, we identified several potential DEC1 responsive elements in the proximal promoter region of the ID1 gene. Moreover, we showed that overexpression of ID1 or ID1', an isoform of ID1, promotes cell proliferation potentially through inhibition of p21 expression. Finally, we found that the extent of DNA damage-induced premature senescence was substantially decreased by overexpression of ID1 or ID1'. Taken together, our study suggests that p53 trans-repressional activity can be mediated by its own target DEC1 and ID1 is an effector of the p53-dependent DNA damage response pathway.
Figures



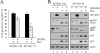
Similar articles
-
DEC1, a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor and a novel target gene of the p53 family, mediates p53-dependent premature senescence.J Biol Chem. 2008 Feb 1;283(5):2896-905. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708624200. Epub 2007 Nov 19. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18025081 Free PMC article.
-
Id1 cooperates with oncogenic Ras to induce metastatic mammary carcinoma by subversion of the cellular senescence response.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 8;105(14):5402-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801505105. Epub 2008 Mar 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18378907 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitor of Differentiation/DNA Binding 1 (ID1) Inhibits Etoposide-induced Apoptosis in a c-Jun/c-Fos-dependent Manner.J Biol Chem. 2016 Mar 25;291(13):6831-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.704361. Epub 2016 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26858249 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitor of Differentiation 1 (Id1) in Cancer and Cancer Therapy.Int J Med Sci. 2020 Apr 6;17(8):995-1005. doi: 10.7150/ijms.42805. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32410828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A History of Cancer Research: The P53 Pathway.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2025 Feb 3;15(2):a035931. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a035931. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2025. PMID: 39900457 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome wide DNA copy number analysis of serous type ovarian carcinomas identifies genetic markers predictive of clinical outcome.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30996. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030996. Epub 2012 Feb 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22355333 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of the inhibitor of DNA binding 1 as a novel marker for radioresistance in pancreatic cancer using genome-wide RNA-seq.Cancer Drug Resist. 2022 Oct 18;5(4):926-938. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2022.60. eCollection 2022. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 36627902 Free PMC article.
-
The bHLH transcription factor DEC1 promotes thyroid cancer aggressiveness by the interplay with NOTCH1.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Aug 29;9(9):871. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0933-y. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30158530 Free PMC article.
-
Id1 expression in kidney endothelial cells protects against diabetes-induced microvascular injury.FEBS Open Bio. 2020 Aug;10(8):1447-1462. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12793. Epub 2020 Jun 26. FEBS Open Bio. 2020. PMID: 31957231 Free PMC article.
-
Smurf2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of Id1 regulates p16 expression during senescence.Aging Cell. 2011 Dec;10(6):1038-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00746.x. Epub 2011 Oct 7. Aging Cell. 2011. PMID: 21933340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Norton, J. D. (2000) J. Cell Sci. 113 3897–3905 - PubMed
-
- Benezra, R., Davis, R. L., Lockshon, D., Turner, D. L., and Weintraub, H. (1990) Cell 61 49–59 - PubMed
-
- Ellis, H. M., Spann, D. R., and Posakony, J. W. (1990) Cell 61 27–38 - PubMed
-
- Garrell, J., and Modolell, J. (1990) Cell 61 39–48 - PubMed
-
- Ouyang, X. S., Wang, X., Lee, D. T., Tsao, S. W., and Wong, Y. C. (2002) J. Urol. 167 2598–2602 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

