Depletion of resident alveolar macrophages does not prevent Fas-mediated lung injury in mice
- PMID: 18556802
- PMCID: PMC2519850
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00210.2007
Depletion of resident alveolar macrophages does not prevent Fas-mediated lung injury in mice
Abstract
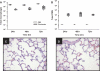
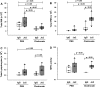
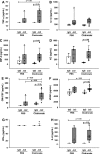
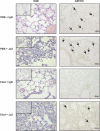
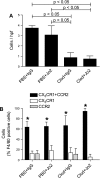
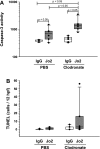
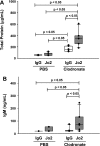
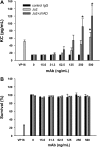
Activation of the Fas/Fas ligand (FasL) system in the lungs results in a form of injury characterized by alveolar epithelial apoptosis and neutrophilic inflammation. Studies in vitro show that Fas activation induces apoptosis in alveolar epithelial cells and cytokine production in alveolar macrophages. The main goal of this study was to determine the contribution of alveolar macrophages to Fas-induced lung inflammation in mice, by depleting alveolar macrophages using clodronate-containing liposomes. Liposomes containing clodronate or PBS were instilled by intratracheal instillation. After 24 h, the mice received intratracheal instillations of the Fas-activating monoclonal antibody Jo2 or an isotype control antibody and were studied 18 h later. The Jo2 MAb induced increases in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) total neutrophils, lung caspase-3 activity, and BALF total protein and worsened histological lung injury in the macrophage-depleted mice. Studies in vitro showed that Fas activation induced the release of the cytokine KC in a mouse lung epithelial cell line, MLE-12. These results suggest that the lung inflammatory response to Fas activation is not primarily dependent on resident alveolar macrophages and may instead depend on cytokine release by alveolar epithelial cells.
Figures
References
-
- Austyn JM, Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol 11: 805–815, 1981. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

