The glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor: a complex membrane-anchoring structure for proteins
- PMID: 18557633
- PMCID: PMC2663890
- DOI: 10.1021/bi8006324
The glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor: a complex membrane-anchoring structure for proteins
Abstract
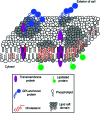
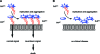
Positioned at the C-terminus of many eukaryotic proteins, the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor is a posttranslational modification that anchors the modified protein in the outer leaflet of the cell membrane. The GPI anchor is a complex structure comprising a phosphoethanolamine linker, glycan core, and phospholipid tail. GPI-anchored proteins are structurally and functionally diverse and play vital roles in numerous biological processes. While several GPI-anchored proteins have been characterized, the biological functions of the GPI anchor have yet to be elucidated at a molecular level. This review discusses the structural diversity of the GPI anchor and its putative cellular functions, including involvement in lipid raft partitioning, signal transduction, targeting to the apical membrane, and prion disease pathogenesis. We specifically highlight studies in which chemically synthesized GPI anchors and analogues have been employed to study the roles of this unique posttranslational modification.
Figures


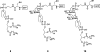
References
-
- Nosjean O.; Briolay A.; Roux B. (1997) Mammalian GPI proteins: sorting, membrane residence and functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1331, 153–186. - PubMed
-
- Low M. (1999) GPI-anchored biomolecules—an overview, in GPI-anchored membrane proteins and carbohydrates (Hoessli D. C., and Ilangumaran S., Eds.) pp. 1−14, Landes Company, Austin, TX.
-
- Ferguson M. A. (1999) The structure, biosynthesis and functions of glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors, and the contributions of trypanosome research. J. Cell Sci. 112, 2799–2809. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson M. A.; Homans S. W.; Dwek R. A.; Rademacher T. W. (1988) Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol moiety that anchors Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein to the membrane. Science 239, 753–759. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson M. A.; Low M. G.; Cross G. A. (1985) Glycosyl-sn-1,2-dimyristylphosphatidylinositol is covalently linked to Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 14547–14555. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

