Targeting the chemotactic function of CD147 reduces collagen-induced arthritis
- PMID: 18557953
- PMCID: PMC2632695
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02877.x
Targeting the chemotactic function of CD147 reduces collagen-induced arthritis
Abstract
CD147 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein expressed on a wide variety of cell types, including all leucocytes. While CD147 is best known as a potent inducer of matrix metalloproteinases, it can also function as a regulator of leucocyte migration through its cell surface interaction with chemotactic extracellular cyclophilins. A potential role for CD147-cyclophilin interactions during inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), is suggested from several studies. For example, CD147 expression is increased on reactive leucocytes in the synovial fluid and tissues of patients with arthritis. In addition, the synovial fluid of patients with RA contains high levels of extracellular cyclophilin A. In the current studies we investigated the contribution of the chemotactic function of CD147-cyclophilin interactions to joint inflammation using the mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis. Our data demonstrate that proinflammatory leucocytes, specifically neutrophils, monocytes and activated CD4(+) T cells, lose their ability to migrate in response to cyclophilin A in vitro when treated with anti-CD147 monoclonal antibody. Furthermore, in vivo treatment with anti-CD147 monoclonal antibody can reduce the development of collagen-induced arthritis in mice by >75%. Such findings suggest that CD147-cyclophilin interactions might contribute to the pathogenesis of RA by promoting the recruitment of leucocytes into joint tissues.
Figures
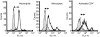
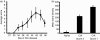
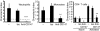
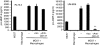

References
-
- Firestein GS. Invasive fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Passive responders or transformed aggressors? Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39:1781–90. - PubMed
-
- Choy EH, Panayi GS. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:907–16. - PubMed
-
- Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:397–440. - PubMed
-
- Nabeshima K, Iwasaki H, Koga K, Hojo H, Suzumiya J, Kikuchi M. Emmprin (basigin/CD147): matrix metalloproteinase modulator and multifunctional cell recognition molecule that plays a critical role in cancer progression. Pathol Int. 2006;56:359–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

