Serotonin type 1D receptors (5HTR) are differentially distributed in nerve fibres innervating craniofacial tissues
- PMID: 18557979
- PMCID: PMC2682350
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01635.x
Serotonin type 1D receptors (5HTR) are differentially distributed in nerve fibres innervating craniofacial tissues
Abstract
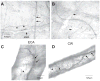
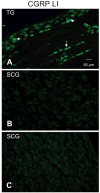
We tested the hypothesis that the 5HT(1D)R, the primary antinociceptive target of triptans, is differentially distributed in tissues responsible for migraine pain. The density of 5HT(1D)R was quantified in tissues obtained from adult female rats with Western blot analysis. Receptor location was assessed with immunohistochemistry. The density of 5HT(1D)R was significantly greater in tissues known to produce migraine-like pain (i.e. circle of Willis and dura) than in structures in which triptans have no antinociceptive efficacy (i.e. temporalis muscle). 5HT(1D)R-like immunoreactivity was restricted to neuronal fibres, where it colocalized with calcitonin gene-related peptide and tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive fibres. These results are consistent with our hypothesis that the limited therapeutic profile of triptans could reflect its differential peripheral distribution and that the antinociceptive efficacy reflects inhibition of neuropeptide release from sensory afferents. An additional site of action at sympathetic efferents is also suggested.
Figures





References
-
- Waeber C, Moskowitz MA. Therapeutic implications of central and peripheral neurologic mechanisms in migraine. Neurology. 2003;61:S9–20. - PubMed
-
- Ottani A, Ferraris E, Giuliani D, Mioni C, Bertolini A, Sternieri E, Ferrari A. Effect of sumatriptan in different models of pain in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;497:181–6. - PubMed
-
- Cumberbatch MJ, Hill RG, Hargreaves RJ. Differential effects of the 5HT1B/1D receptor agonist naratriptan on trigeminal versus spinal nociceptive responses. Cephalalgia. 1998;18:659–63. - PubMed
-
- Dao TT, Lund JP, Remillard G, Lavigne GJ. Is myofascial pain of the temporal muscles relieved by oral sumatriptan? A cross-over pilot study. Pain. 1995;62:241–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

