Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase in development and disease: sphingolipid metabolism takes flight
- PMID: 18558101
- PMCID: PMC2749932
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2008.05.005
Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase in development and disease: sphingolipid metabolism takes flight
Abstract
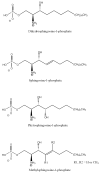
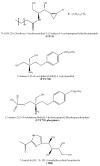
Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase (SPL) is a highly conserved enzyme that catalyses the final step of sphingolipid degradation, namely the irreversible cleavage of the carbon chain at positions 2-3 of a long-chain base phosphate (LCBP), thereby yielding a long-chain aldehyde and phosphoethanolamine. LCBPs are potent signaling molecules involved in cell proliferation, survival, migration, cell-cell interactions and cell stress responses. Therefore, tight regulation of LCBP signaling is required for proper cell function, and perturbations of this system can lead to alterations in biological processes including development, reproduction and physiology. SPL is a key enzyme in regulating the intracellular and circulating levels of LCBPs and is, therefore, gaining attention as a putative target for pharmacological intervention. This review provides an overview of our current understanding of SPL structure and function, mechanisms involved in SPL regulation and the role of SPL in development and disease.
Figures




References
-
- Hannun YA, Luberto C, Argraves KM. Enzymes of sphingolipid metabolism: from modular to integrative signaling. Biochemistry. 2001;40:4893–4903. - PubMed
-
- Gómez-Muñoz A, Kong J, Parhar K, Wang S, Gangoiti P, González M, Eivemark S, Salh B, Duronio V, Steinbrecher U. Ceramide-1-phosphate promotes cell survival through activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:3744–3750. - PubMed
-
- Wijesinghe D, Lamour N, Gomez-Munoz A, Chalfant C. Ceramide kinase and ceramide-1-phosphate. Methods Enzymol. 2007;434:265–292. - PubMed
-
- Gardell S, Dubin A, Chun J. Emerging medicinal roles for lysophospholipid signaling. Trends Mol Med. 2006;12:65–75. - PubMed
-
- Karliner J. Mechanisms of cardioprotection by lysophospholipids. J Cell Biochem. 2004;92:1095–1103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

