An in vitro comparison of microdialysis relative recovery of Met- and Leu-enkephalin using cyclodextrins and antibodies as affinity agents
- PMID: 18558138
- PMCID: PMC2519001
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2008.05.028
An in vitro comparison of microdialysis relative recovery of Met- and Leu-enkephalin using cyclodextrins and antibodies as affinity agents
Abstract
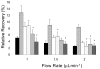
Cyclodextrins and antibodies have been used as affinity agents to improve relative recovery during microdialysis sampling. Two neuropeptides, methionine-enkephalin (ME) and leucine-enkephalin (LE), were chosen to compare the use of cyclodextrins and antibodies as possible affinity agents for improving their relative recovery across polycarbonate and polyethersulfone membranes during in vitro sampling. Cyclodextrins (CD) including beta-CD, 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (2HPbeta-CD), and gamma-CD gave improvements of relative recovery for both peptides of less than 2-fold as compared to controls. Comparisons of relative recovery between tyrosine-glycine-glycine, tyrosine, and phenylalanine using different cyclodextrins in the perfusion fluid were also obtained. Inclusion of an antibody against met-enkephalin in the microdialysis perfusion fluid resulted in relative recovery increases of up to 2.5-fold. These results show that using antibodies as affinity agents during microdialysis sampling may be more effective agents to improve the relative recovery of these opioid neuropeptides.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Water-soluble cyclodextrin polymers for enhanced relative recovery of hydrophobic analytes during microdialysis sampling.Analyst. 2003 Sep;128(9):1143-9. doi: 10.1039/b308057a. Analyst. 2003. PMID: 14529021
-
Immunohistochemical investigation of enkephalins in the human inner ear.Hear Res. 1998 Apr;118(1-2):123-8. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5955(98)00023-9. Hear Res. 1998. PMID: 9606067
-
A new electrochemical HPLC method for analysis of enkephalins and endomorphins.J Neurosci Methods. 2006 Jan 15;150(1):74-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2005.06.001. Epub 2005 Jul 26. J Neurosci Methods. 2006. PMID: 16051372
-
Natural and synthetic affinity agents as microdialysis sampling mass transport enhancers: current progress and future perspectives.Biosens Bioelectron. 2006 Sep 15;22(3):449-57. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2006.05.004. Epub 2006 Jun 23. Biosens Bioelectron. 2006. PMID: 16797961 Review.
-
Peripheral actions of opiates in canine gastrointestinal tract: actions on nerves and muscles.Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1987;11(3 Pt 2):35B-43B. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1987. PMID: 2886394 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A rapid screening method to select microdialysis carriers for hydrophobic compounds.PLoS One. 2021 Sep 1;16(9):e0256920. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256920. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34469501 Free PMC article.
-
Electroosmotic perfusion of tissue: sampling the extracellular space and quantitative assessment of membrane-bound enzyme activity in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014 Oct;406(26):6455-68. doi: 10.1007/s00216-014-8067-2. Epub 2014 Aug 29. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014. PMID: 25168111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Numerical Modeling of Electroosmotic Push-Pull Perfusion and Assessment of Its Application to Quantitative Determination of Enzymatic Activity in the Extracellular Space of Mammalian Tissue.Anal Chem. 2017 Jun 6;89(11):5864-5873. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00187. Epub 2017 May 11. Anal Chem. 2017. PMID: 28447456 Free PMC article.
-
Methods of Measuring Enzyme Activity Ex Vivo and In Vivo.Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2018 Jun 12;11(1):509-533. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-061417-125619. Epub 2018 Mar 5. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2018. PMID: 29505726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel microemulsion-based isotonic perfusate modulated by Ringer's solution for improved microdialysis recovery of liposoluble substances.J Nanobiotechnology. 2018 Nov 14;16(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s12951-018-0418-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018. PMID: 30428875 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

