Mechanisms and strategies for effective delivery of antisense and siRNA oligonucleotides
- PMID: 18558618
- PMCID: PMC2475625
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn342
Mechanisms and strategies for effective delivery of antisense and siRNA oligonucleotides
Abstract
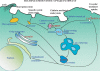
The potential use of antisense and siRNA oligonucleotides as therapeutic agents has elicited a great deal of interest. However, a major issue for oligonucleotide-based therapeutics involves effective intracellular delivery of the active molecules. In this Survey and Summary, we review recent reports on delivery strategies, including conjugates of oligonucleotides with various ligands, as well as use of nanocarrier approaches. These are discussed in the context of intracellular trafficking pathways and issues regarding in vivo biodistribution of molecules and nanoparticles. Molecular-sized chemical conjugates and supramolecular nanocarriers each display advantages and disadvantages in terms of effective and nontoxic delivery. Thus, choice of an optimal delivery modality will likely depend on the therapeutic context.
Figures


References
-
- Nahta R, Esteva FJ. Bcl-2 antisense oligonucleotides: a potential novel strategy for the treatment of breast cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2003;30:143–149. - PubMed
-
- Dean NM, Bennett CF. Antisense oligonucleotide-based therapeutics for cancer. Oncogene. 2003;22:9087–9096. - PubMed
-
- Chan JH, Lim S, Wong WS. Antisense oligonucleotides: from design to therapeutic application. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006;33:533–540. - PubMed
-
- Coppelli FM, Grandis JR. Oligonucleotides as anticancer agents: from the benchside to the clinic and beyond. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005;11:2825–2840. - PubMed
-
- Manoharan M. Oligonucleotide conjugates as potential antisense drugs with improved uptake, biodistribution, targeted delivery, and mechanism of action. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 2002;12:103–128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

