Xanthones from the botanical dietary supplement mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana) with aromatase inhibitory activity
- PMID: 18558747
- PMCID: PMC2572570
- DOI: 10.1021/np8000255
Xanthones from the botanical dietary supplement mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana) with aromatase inhibitory activity
Abstract
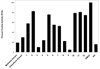
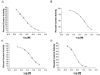
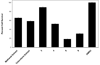
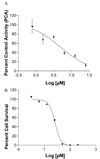
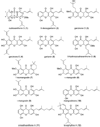
Twelve xanthone constituents of the botanical dietary supplement mangosteen (the pericarp of Garcinia mangostana) were screened using a noncellular, enzyme-based microsomal aromatase inhibition assay. Of these compounds, garcinone D (3), garcinone E (5), alpha-mangostin (8), and gamma-mangostin (9) exhibited dose-dependent inhibitory activity. In a follow-up cell-based assay using SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells that express high levels of aromatase, the most potent of these four xanthones was gamma-mangostin (9). Because xanthones may be consumed in substantial amounts from commercially available mangosteen products, the consequences of frequent intake of mangosteen botanical dietary supplements require further investigation to determine their possible role in breast cancer chemoprevention.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antioxidant xanthones from the pericarp of Garcinia mangostana (Mangosteen).J Agric Food Chem. 2006 Mar 22;54(6):2077-82. doi: 10.1021/jf052649z. J Agric Food Chem. 2006. PMID: 16536578
-
The purple mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana): Defining the anticancer potential of selected xanthones.Pharmacol Res. 2022 Jan;175:106032. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.106032. Epub 2021 Dec 9. Pharmacol Res. 2022. PMID: 34896543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LC-QTOF-MS analysis of xanthone content in different parts of Garcinia mangostana and its influence on cholinesterase inhibition.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020 Dec;35(1):1433-1441. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1786819. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32608273 Free PMC article.
-
Prenylated xanthones from mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana) target oxidative mitochondrial respiration in cancer cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Oct;179:117365. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117365. Epub 2024 Aug 31. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39217837
-
Garcinia mangostana L.: a phytochemical and pharmacological review.Phytother Res. 2009 Aug;23(8):1047-65. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2730. Phytother Res. 2009. PMID: 19172667 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined extracts of Garcinia mangostana fruit rind and Cinnamomum tamala leaf supplementation enhances muscle strength and endurance in resistance trained males.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018 Oct 22;15(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12970-018-0257-4. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30348185 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Xanthones from the Leaves of Garcinia cowa Induce Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis, and Autophagy in Cancer Cells.Molecules. 2015 Jun 19;20(6):11387-99. doi: 10.3390/molecules200611387. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26102071 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the antineoplastic potential of α-mangostin in breast cancer.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2025 Jul 3;15(1):43. doi: 10.1007/s13659-025-00528-5. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2025. PMID: 40608162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural compounds with aromatase inhibitory activity: an update.Planta Med. 2010 Aug;76(11):1087-93. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1250169. Epub 2010 Jul 15. Planta Med. 2010. PMID: 20635310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mangosteen pericarp extract inhibits the formation of pentosidine and ameliorates skin elasticity.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2015 Jul;57(1):27-32. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.15-13. Epub 2015 Apr 16. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26236097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM. Lancet Oncol. 2001;2:533–543. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2007;57:43–66. - PubMed
-
- Osborne CK, Schiff R, Fuqua SAW, Shou J. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001;7:4338s–4342s. - PubMed
-
- Brueggemeier RW, Richards JA, Petrel TA. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003;86:501–507. - PubMed
-
- Kuller LH, Matthews KA, Meilahn EN. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000;74:297–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

