Genetic diversity and antimicrobial resistance in group B streptococcus colonizing young, nonpregnant women
- PMID: 18558880
- PMCID: PMC9491395
- DOI: 10.1086/589864
Genetic diversity and antimicrobial resistance in group B streptococcus colonizing young, nonpregnant women
Abstract
The genetic diversity of group B Streptococcus in young, nonpregnant women is not well studied. Application of multilocus sequence analysis to 85 group B Streptococcus strains recovered from college students revealed similarities and differences in distribution of group B Streptococcus lineages, compared with that of previously studied pregnant populations, and revealed that strains of 1 clone were associated with antibiotic resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
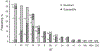
References
-
- Davies HD, Adair C, McGeer A, et al. Antibodies to capsular polysaccharides of group B Streptococcus in pregnant Canadian women: relationship to colonization status and infection in the neonate. J Infect Dis 2001; 184:285–91. - PubMed
-
- Manning SD, Neighbors K, Tallman PA, et al. Prevalence of group B Streptococcus colonization and potential for transmission by casual contact in healthy young men and women. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39:380–8. - PubMed
-
- Zaleznik DF, Rench MA, Hillier S, et al. Invasive disease due to group B Streptococcus in pregnant women and neonates from diverse population groups. Clin Infect Dis 2000;30:276–81. - PubMed
-
- Harrison LH, Elliott JA, Dwyer DM, et al. Serotype distribution of invasive group B streptococcal isolates in Maryland: implications for vaccine formulation. J Infect Dis 1998; 177:998–1002. - PubMed

