Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and ErbB kinase inhibitor combinations block proliferation and induce apoptosis through cyclin D1 reduction and Bax activation
- PMID: 18559346
- PMCID: PMC3259780
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M708360200
Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and ErbB kinase inhibitor combinations block proliferation and induce apoptosis through cyclin D1 reduction and Bax activation
Abstract
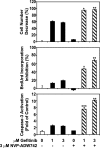
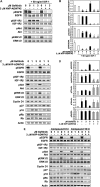
The insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) and ErbB family of receptors are receptor tyrosine kinases that play important roles in cancer. Lack of response and resistance to therapies targeting ErbB receptors occur and are often associated with activation of the IGF-1R pathway. Combinations of agents that inhibit IGF-1R and ErbB receptors have been shown to synergistically block cancer cell proliferation and xenograft tumor growth. To determine the mechanism by which targeting both IGF-1R and ErbB receptors causes synergistic effects on cell growth and survival, we investigated the effects of combinations of selective IGF-1R and ErbB kinase inhibitors on proliferative and apoptotic signaling. We identified A431 squamous cell carcinoma cells as most sensitive to combinations of ErbB and IGF-1R inhibitors. The inhibitor combinations resulted in not only blockade of A431 cell proliferation, but also induced apoptosis, which was not seen with either agent alone. Upon examining phosphorylation states and expression levels of proteins in the IGF-1R and ErbB signaling pathways, we found a correlation between the ability of combinations to inhibit proliferation and to decrease levels of phosphorylated Akt and cyclin D1. In addition, the massive cell death induced by combined IGF-1R/ErbB inhibition was associated with Mcl-1 reduction and Bax activation. Thus, targeting both IGF-1R and ErbB receptors simultaneously results in cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through combined effects on Akt, cyclin D1, and Bax activation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor inhibition induces a resistance mechanism via the epidermal growth factor receptor/HER3/AKT signaling pathway: rational basis for cotargeting insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor in hepatocellular carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Sep 1;15(17):5445-56. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2980. Epub 2009 Aug 25. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19706799
-
MicroRNA-302b-3p Suppresses Cell Proliferation Through AKT Pathway by Targeting IGF-1R in Human Gastric Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(4):1701-1711. doi: 10.1159/000479419. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28743112
-
HER receptor signaling confers resistance to the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibitor, BMS-536924.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Sep;7(9):2589-98. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0493. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18765823 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1 and oestradiol promote cell proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells: new insights into their synergistic effects.Mol Pathol. 2001 Jun;54(3):149-54. doi: 10.1136/mp.54.3.149. Mol Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11376126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy: advances and perspectives.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(20):2901-13. doi: 10.2174/138161212800672723. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22571659 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential induction of apoptosis in HER2 and EGFR addicted cancers following PI3K inhibition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Nov 17;106(46):19503-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0905056106. Epub 2009 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19850869 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor induces resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor antagonism in head and neck squamous carcinoma cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Nov;10(11):2124-34. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0294. Epub 2011 Aug 30. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21878657 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-503 acts as a tumor suppressor in glioblastoma for multiple antitumor effects by targeting IGF-1R.Oncol Rep. 2014 Mar;31(3):1445-52. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2951. Epub 2013 Dec 30. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24378652 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a novel hexavalent humanized anti-IGF-1R antibody and its bivalent parental IgG in diverse cancer cell lines.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44235. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044235. Epub 2012 Aug 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952934 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and its signaling network for the treatment of cancer: current status and future perspectives.Oncol Rev. 2013 Apr 22;7(1):e3. doi: 10.4081/oncol.2013.e3. eCollection 2013 Apr 22. Oncol Rev. 2013. PMID: 25992224 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hofmann, F., and Garcia-Echeverria, C. (2005) Drug Discov. Today 10 1041–1047 - PubMed
-
- Yakar, S., Leroith, D., and Brodt, P. (2005) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16 407–420 - PubMed
-
- Baserga, R. (2005) Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 9 753–768 - PubMed
-
- Hubbard, R. D., and Wilsbacher, J. L. (2007) Chem. Med. Chem. 2 41–46 - PubMed
-
- Bohula, E. A., Playford, M. P., and Macaulay, V. M. (2003) Anticancer Drugs 14 669–682 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

