Matrix metalloproteinase 9 is a mediator of epidermal growth factor-dependent e-cadherin loss in ovarian carcinoma cells
- PMID: 18559505
- PMCID: PMC3621086
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5046
Matrix metalloproteinase 9 is a mediator of epidermal growth factor-dependent e-cadherin loss in ovarian carcinoma cells
Abstract
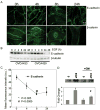
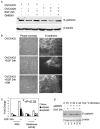
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor (EGFR) is frequently elevated in epithelial ovarian cancer, and E-cadherin expression is often reduced in advanced disease. In this study, we investigated a mechanism by which EGFR activation promotes disruption of adherens junctions through induction of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9). We show that EGFR activation down-modulates E-cadherin, and broad spectrum MMP inhibition ameliorates EGF-stimulated junctional disruption and loss of E-cadherin protein. MMP-9 involvement in EGF-dependent down-regulation of E-cadherin was determined by siRNA specifically directed against MMP-9. Furthermore, treatment with recombinant MMP-9 or transient expression of MMP-9 is sufficient to reduce E-cadherin levels in differentiated ovarian tumor cells. Stable overexpression of MMP-9 led to a loss of E-cadherin and junctional integrity, and promoted a migratory and invasive phenotype. Thus, elevated MMP-9 protein expression is sufficient for junctional disruption and loss of E-cadherin in these cells. The associations between EGFR activation, MMP-9 expression, and E-cadherin were investigated in human ovarian tumors and paired peritoneal metastases wherein immunohistochemical staining for activated (phospho) EGFR and MMP-9 colocalized with regions of reduced E-cadherin. These data suggest that regulation of MMP-9 by EGFR may represent a novel mechanism for down-modulation of E-cadherin in ovarian cancer.
Figures




References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56:106–30. - PubMed
-
- Mendelsohn J, Baselga J. Status of epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists in the biology and treatment of cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2787–99. - PubMed
-
- Bast RC, Jr, Pusztai L, Kerns BJ, et al. Coexpression of the HER-2 gene product, p185HER-2, and epidermal growth factor receptor, p170EGF-R, on epithelial ovarian cancers and normal tissues. Hybridoma. 1998;17:313–21. - PubMed
-
- Maihle NJ, Baron AT, Barrette BA, et al. EGF/ErbB receptor family in ovarian cancer. Cancer Treat Res. 2002;107:247–58. - PubMed
-
- Perez-Soler R. HER1/EGFR targeting: refining the strategy. Oncologist. 2004;9:58–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

