Role of acetylation and extracellular location of heat shock protein 90alpha in tumor cell invasion
- PMID: 18559531
- PMCID: PMC2665713
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0644
Role of acetylation and extracellular location of heat shock protein 90alpha in tumor cell invasion
Abstract
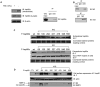
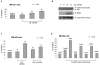
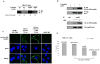
Heat shock protein (hsp) 90 is an ATP-dependent molecular chaperone that maintains the active conformation of client oncoproteins in cancer cells. An isoform, hsp90alpha, promotes extracellular maturation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, involved in tumor invasion and metastasis. Knockdown of histone deacetylase (HDAC) 6, which deacetylates lysine residues in hsp90, induces reversible hyperacetylation and attenuates ATP binding and chaperone function of hsp90. Here, using mass spectrometry, we identified seven lysine residues in hsp90alpha that are hyperacetylated after treatment of eukaryotic cells with a pan-HDAC inhibitor that also inhibits HDAC6. Depending on the specific lysine residue in the middle domain involved, although acetylation affects ATP, cochaperone, and client protein binding to hsp90alpha, acetylation of all seven lysines increased the binding of hsp90alpha to 17-allyl-amino-demethoxy geldanamycin. Notably, after treatment with the pan-HDAC inhibitor panobinostat (LBH589), the extracellular hsp90alpha was hyperacetylated and it bound to MMP-2, which was associated with increased in vitro tumor cell invasiveness. Treatment with antiacetylated hsp90alpha antibody inhibited in vitro invasion by tumor cells. Thus, reversible hyperacetylation modulates the intracellular and extracellular chaperone function of hsp90, and targeting extracellular hyperacetylated hsp90alpha may undermine tumor invasion and metastasis.
Figures



References
-
- Whitesell L, Lindquist SL. Hsp90 and the chaperoning of cancer. Nature Rev Cancer. 2005;5:761–72. - PubMed
-
- Isaacs J, Xu W, Neckers L. Heat shock protein 90 as a molecular target for cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell. 2003;3:213–17. - PubMed
-
- Panaretou B, Siligardi G, Meyer P, et al. Activation of the ATPase activity of hsp90 by the stress-regulated cochaperone Aha1. Molec Cell. 2002;10:1307–18. - PubMed
-
- Morishima Y, Kanelakis KC, Murphy PJ, et al. The hsp90 cochaperone p23 is the limiting component of the multiprotein hsp90/hsp70-based chaperone system in vivo where it acts to stabilize the client protein hsp90 complex. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:48754–63. - PubMed
-
- Roe S, Ali MM, Meyer P, et al. The mechanism of hsp90 regulation by the protein kinase-specific cochaperone p50cdc37. Cell. 2004;116:87–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

