Overexpression of CDC25B and LAMC2 mRNA and protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas and premalignant lesions in subjects from a high-risk population in China
- PMID: 18559558
- PMCID: PMC2729558
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-0666
Overexpression of CDC25B and LAMC2 mRNA and protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas and premalignant lesions in subjects from a high-risk population in China
Abstract
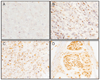
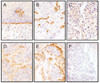
Molecular events associated with the initiation and progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) remain poorly understood but likely hold the key to effective early detection approaches for this almost invariably fatal cancer. CDC25B and LAMC2 are two promising early detection candidates emerging from new molecular studies of ESCC. To further elucidate the role of these two genes in esophageal carcinogenesis, we did a series of studies to (a) confirm RNA overexpression, (b) establish the prevalence of protein overexpression, (c) relate protein overexpression to survival, and (d) explore their potential as early detection biomarkers. Results of these studies indicated that CDC25B mRNA was overexpressed (>/=2-fold overexpression in tumor compared with normal) in 64% of the 73 ESCC cases evaluated, whereas LAMC2 mRNA was overexpressed in 89% of cases. CDC25B protein expression was categorized as positive in 59% (144 of 243) of ESCC cases on a tumor tissue microarray, and nonnegative LAMC2 patterns of protein expression were observed in 82% (225 of 275) of cases. Multivariate-adjusted proportional hazard regression models showed no association between CDC25B protein expression score and risk of death [hazard ratio (HR) for each unit increase in expression score, 1.00; P = 0.90]; however, several of the LAMC2 protein expression patterns strongly predicted survival. Using the cytoplasmic pattern as the reference (the pattern with the lowest mortality), cases with a diffuse pattern had a 254% increased risk of death (HR, 3.52; P = 0.007), cases with no LAMC2 expression had a 169% increased risk of death (HR, 2.69; P = 0.009), and cases with a peripheral pattern had a 130% greater risk of death (HR, 2.30; P = 0.02). CDC25B protein expression scores in subjects with esophageal biopsies diagnosed as normal (n = 35), dysplastic (n = 23), or ESCC (n = 32) increased significantly with morphologic progression. For LAMC2, all normal and dysplastic patients had a continuous pattern of protein expression, whereas all ESCCs showed alternative, noncontinuous patterns. This series of studies showed that both CDC25B and LAMC2 overexpress RNA and protein in a significant majority of ESCC cases. The strong relation of LAMC2 pattern of protein expression to survival suggests a role in prognosis, whereas the association of CDC25B with morphologic progression indicates a potential role as an early detection marker.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of differentially expressed genes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) by cDNA expression array: overexpression of Fra-1, Neogenin, Id-1, and CDC25B genes in ESCC.Clin Cancer Res. 2001 Aug;7(8):2213-21. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11489794
-
Expression and significance of CDC25B, PED/PEA-15 in esophageal carcinoma.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2015 Apr;30(3):139-45. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2014.1701. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2015. PMID: 25775393 Clinical Trial.
-
MiR-214 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting CDC25B.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Nov;95:1678-1683. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.09.048. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28954387
-
Clinical significance of CDC25A and CDC25B expression in squamous cell carcinomas of the oesophagus.Br J Cancer. 2001 Aug 3;85(3):412-21. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.2001.1934. Br J Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11487274 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between the expression of hTERT and EYA4 mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells with the progressive stages of carcinogenesis of the esophagus.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Nov 25;28(1):145. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-28-145. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19939248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Secreted protein profiling of human aortic smooth muscle cells identifies vascular disease associations.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 10:2023.11.10.23298351. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.10.23298351. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024 Apr;44(4):898-914. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.123.320274. PMID: 37986932 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Image microarrays derived from tissue microarrays (IMA-TMA): New resource for computer-aided diagnostic algorithm development.J Pathol Inform. 2012;3:24. doi: 10.4103/2153-3539.98168. Epub 2012 Jul 12. J Pathol Inform. 2012. PMID: 22934237 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic characterization of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma from a high-risk population in China.Cancer Res. 2009 Jul 15;69(14):5908-17. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4622. Epub 2009 Jul 7. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19584285 Free PMC article.
-
Multiomics dynamic learning enables personalized diagnosis and prognosis for pancancer and cancer subtypes.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Sep 22;24(6):bbad378. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad378. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37889117 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial transcriptomics analysis of esophageal squamous precancerous lesions and their progression to esophageal cancer.Nat Commun. 2023 Aug 8;14(1):4779. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40343-5. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37553345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Cancer Control Office. Investigation of cancer mortality in China. China: People's Health Publishing House, Beijing; 1980.
-
- Li JY. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer in China. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1982;62:113–120. - PubMed
-
- Su H, Hu N, Shih J, et al. Gene expression analysis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma reveals consistent molecular profiles related to a family history of upper gastrointestinal cancer. Cancer Res. 2003;63:3872–3876. - PubMed
-
- Galaktionov K, Beach D. Specific activation of cdc25 tyrosine phosphatases by B-type cyclins: evidence for multiple roles of mitotic cyclins. Cell. 1991;67:1181–1194. - PubMed
-
- Demetrick DJ, Beach DH. Chromosome mapping of human CDC25A and CDC25B phosphatases. Genomics. 1993;18:144–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

