A physiologic index of comorbidity: relationship to mortality and disability
- PMID: 18559635
- PMCID: PMC2496995
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/63.6.603
A physiologic index of comorbidity: relationship to mortality and disability
Abstract
Background: In older adults, there is often substantial undiagnosed chronic disease detectable on noninvasive testing, not accounted for by most comorbidity indices. We developed a simple physiologic index of comorbidity by scoring five noninvasive tests across the full range of values. We examined the predictive validity of this index for mortality and disability.
Methods: There were 2928 (mean age 74.5 years, 60% women, 85% white, and 15% black) participants in the Cardiovascular Health Study (1992-1993) who had carotid ultrasound, pulmonary function testing, brain magnetic resonance scan, serum cystatin-C, and fasting glucose. These were combined into a single physiologic index of comorbid chronic disease on a scale of 0-10. Cox proportional hazard models were used to predict mortality, mobility limitation, and activities of daily living (ADL) difficulty after a maximum of 9 years.
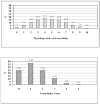
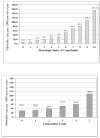
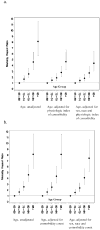
Results: The range of the physiologic index was quite broad, with very few individuals having total scores of either 0 or 10. Those with an index of 7-10 had a hazard ratio of 3.80 (95% confidence interval, 2.82-5.13) for mortality compared to those with scores of 0-2, after adjustment for demographics, behavioral risk factors, and clinically diagnosed conditions. Associations with mobility limitation and ADL difficulty were also significant. The index explained about 40% of the age effect on mortality risk.
Conclusion: Older adults with low levels of markers of chronic disease are rather rare but have remarkably good health outcomes. The ability of such an index to distinguish usual from low risk might provide an opportunity to better understand optimal health in old age.
Figures

References
-
- Hoffman C, Rice D, Sung HY. Persons with chronic conditions. Their prevalence and costs. JAMA. 1996;276:1473–1479. - PubMed
-
- Sachdev M, Sun JL, Tsiatis AA, Nelson CL, Mark DB, Jollis JG. The prognostic importance of comorbidity for mortality in patients with stable coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:576–582. - PubMed
-
- Guralnik JM, LaCroix AZ, Everett DF, Kovar MG. Aging in the eighties: the prevalence of comorbidity and its association with disability. Adv Data. 1989;170:1–8.
-
- Charlson ME, Sax FL, MacKenzie R, Fields SD, Braham RL, Douglass RG., Jr Assessing illness severity: does clinical judgement work? J Chronic Dis. 1986;39:439–452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 AG024827/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5-P30-AG-024827/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85086/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-55222/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC045133/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC035129/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC015103/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-75150/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AG-023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85079/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC075150/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

