Inhibition of OXA-1 beta-lactamase by penems
- PMID: 18559643
- PMCID: PMC2533510
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01677-07
Inhibition of OXA-1 beta-lactamase by penems
Abstract
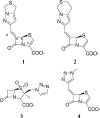
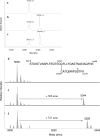
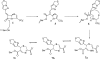
The partnering of a beta-lactam with a beta-lactamase inhibitor is a highly effective strategy that can be used to combat bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics mediated by serine beta-lactamases (EC 3.2.5.6). To this end, we tested two novel penem inhibitors against OXA-1, a class D beta-lactamase that is resistant to inactivation by tazobactam. The K(i) of each penem inhibitor for OXA-1 was in the nM range (K(i) of penem 1, 45 +/- 8 nM; K(i) of penem 2, 12 +/- 2 nM). The first-order rate constant for enzyme and inhibitor complex inactivation of penems 1 and 2 for OXA-1 beta-lactamase were 0.13 +/- 0.01 s(-1) and 0.11 +/- 0.01 s(-1), respectively. By using an inhibitor-to-enzyme ratio of 1:1, 100% inactivation was achieved in <or=900 s and the recovery of OXA-1 beta-lactamase activity was not detected at 24 h. Covalent adducts of penems 1 and 2 (changes in molecular masses, +306 +/- 3 and +321 +/- 3 Da, respectively) were identified by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS). After tryptic digestion of OXA-1 inactivated by penems 1 and 2, ESI-MS and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight MS identified the adducts of 306 +/- 3 and 321 +/- 3 Da attached to the peptide containing the active-site Ser67. The base hydrolysis of penem 2, monitored by serial (1)H nuclear magnetic resonance analysis, suggested that penem 2 formed a linear imine species that underwent 7-endo-trig cyclization to ultimately form a cyclic enamine, the 1,4-thiazepine derivative. Susceptibility testing demonstrated that the penem inhibitors at 4 mg/liter effectively restored susceptibility to piperacillin. Penem beta-lactamase inhibitors which demonstrate high affinities and which form long-lived acyl intermediates may prove to be extremely useful against the broad range of inhibitor-resistant serine beta-lactamases present in gram-negative bacteria.
Figures


References
-
- Barlow, M., and B. G. Hall. 2002. Phylogenetic analysis shows that the OXA β-lactamase genes have been on plasmids for millions of years. J. Mol. Evol. 55:314-321. - PubMed
-
- Beadle, B. M., I. Trehan, P. J. Focia, and B. K. Shoichet. 2002. Structural milestones in the reaction pathway of an amide hydrolase: substrate, acyl, and product complexes of cephalothin with AmpC β-lactamase. Structure 10:413-424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

