Spatial mapping of splicing factor complexes involved in exon and intron definition
- PMID: 18559666
- PMCID: PMC2426932
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200710051
Spatial mapping of splicing factor complexes involved in exon and intron definition
Abstract
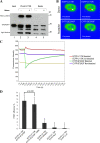
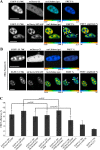
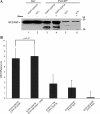
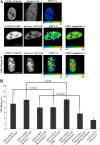
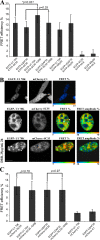
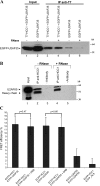
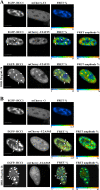
We have analyzed the interaction between serine/arginine-rich (SR) proteins and splicing components that recognize either the 5' or 3' splice site. Previously, these interactions have been extensively characterized biochemically and are critical for both intron and exon definition. We use fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) microscopy to identify interactions of individual SR proteins with the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP)-associated 70-kD protein (U1 70K) and with the small subunit of the U2 snRNP auxiliary factor (U2AF35) in live-cell nuclei. We find that these interactions occur in the presence of RNA polymerase II inhibitors, demonstrating that they are not exclusively cotranscriptional. Using FRET imaging by means of fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM), we map these interactions to specific sites in the nucleus. The FLIM data also reveal a previously unknown interaction between HCC1, a factor related to U2AF65, with both subunits of U2AF. Spatial mapping using FLIM-FRET reveals differences in splicing factors interactions within complexes located in separate subnuclear domains.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interactions of SR45, an SR-like protein, with spliceosomal proteins and an intronic sequence: insights into regulated splicing.Plant J. 2012 Sep;71(6):936-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.05042.x. Epub 2012 Jun 28. Plant J. 2012. PMID: 22563826
-
Reconstitution of exon-bridging activity with purified U2AF and U1 snRNP components.Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1995;(33):218-9. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1995. PMID: 8643375
-
U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle (snRNP) auxiliary factor of 65 kDa, U2AF65, can promote U1 snRNP recruitment to 5' splice sites.Biochem J. 2003 May 15;372(Pt 1):235-40. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021202. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12558503 Free PMC article.
-
How Are Short Exons Flanked by Long Introns Defined and Committed to Splicing?Trends Genet. 2016 Oct;32(10):596-606. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2016.07.003. Epub 2016 Aug 6. Trends Genet. 2016. PMID: 27507607 Review.
-
An active role for splicing in 3'-end formation.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Jul-Aug;2(4):459-70. doi: 10.1002/wrna.68. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21957037 Review.
Cited by
-
Arsenic-induced SUMO-dependent recruitment of RNF4 into PML nuclear bodies.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Dec;21(23):4227-39. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-05-0449. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20943951 Free PMC article.
-
HuR as a molecular target for cancer therapeutics and immune-related disorders.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Sep;188:114442. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114442. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35817212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Why eukaryotic cells use introns to enhance gene expression: splicing reduces transcription-associated mutagenesis by inhibiting topoisomerase I cutting activity.Biol Direct. 2011 May 18;6:24. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-6-24. Biol Direct. 2011. PMID: 21592350 Free PMC article.
-
Probing nucleic acid interactions and pre-mRNA splicing by Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) microscopy.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Nov 14;13(11):14929-45. doi: 10.3390/ijms131114929. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23203103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear physics: quantitative single-cell approaches to nuclear organization and gene expression.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010;75:113-26. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2010.75.057. Epub 2011 Apr 18. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010. PMID: 21502409 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blencowe, B.J., J.A. Bowman, S. McCracken, and E. Rosonina. 1999. SR-related proteins and the processing of messenger RNA precursors. Biochem. Cell Biol. 77:277–291. - PubMed
-
- Caceres, J.F., S. Stamm, D.M. Helfman, and A.R. Krainer. 1994. Regulation of alternative splicing in vivo by overexpression of antagonistic splicing factors. Science. 265:1706–1709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

