Pyridopyrimidine derivatives as inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide synthesis: Application for treatment of diarrhea
- PMID: 18559851
- PMCID: PMC2448855
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0803096105
Pyridopyrimidine derivatives as inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide synthesis: Application for treatment of diarrhea
Abstract
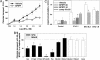
Acute secretory diarrhea induced by infection with enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli involves binding of stable toxin (STa) to its receptor on the intestinal brush border, guanylyl cyclase type C (GC-C). Intracellular cGMP is elevated, inducing increase in chloride efflux and subsequent accumulation of fluid in the intestinal lumen. We have screened a library of compounds and identified a pyridopyrimidine derivatives {5-(3-bromophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-5,11-dihydro-1H-indeno[2',1':5,6]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine-2,4,6-trione; BPIPP} as an inhibitor of GC-C that can suppress STa-stimulated cGMP accumulation by decreasing GC-C activation in intact T84 human colorectal carcinoma cells. BPIPP inhibited stimulation of guanylyl cyclases, including types A and B and soluble isoform in various cells. BPIPP suppressed stimulation of adenylyl cyclase and significantly decreased the activities of adenylyl cyclase toxin of Bordetella pertussis and edema toxin of Bacillus anthracis. The effects of BPIPP on cyclic nucleotide synthesis were observed only in intact cells. The mechanism of BPIPP-dependent inhibition appears to be complex and indirect, possibly associated with phospholipase C and tyrosine-specific phosphorylation. BPIPP inhibited chloride-ion transport stimulated by activation of guanylyl or adenylyl cyclases and suppressed STa-induced fluid accumulation in an in vivo rabbit intestinal loop model. Thus, BPIPP may be a promising lead compound for treatment of diarrhea and other diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
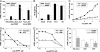
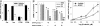

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Heat-Stable Toxin-Induced Intestinal Salt and Water Secretion by a Novel Class of Guanylyl Cyclase C Inhibitors.J Infect Dis. 2015 Dec 1;212(11):1806-15. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv300. Epub 2015 May 21. J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25999056
-
Interruption of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin-induced guanylyl cyclase signaling and associated chloride current in human intestinal cells by 2-chloroadenosine.J Biol Chem. 1997 Jan 10;272(2):754-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.2.754. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 8995360
-
Novel GUCY2C variant causing familial diarrhea in a Mennonite kindred and a potential therapeutic approach.Am J Med Genet A. 2021 Jul;185(7):2046-2055. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62207. Epub 2021 May 5. Am J Med Genet A. 2021. PMID: 33949097 Free PMC article.
-
NIH conference. Cyclic nucleotides: mediators of bacterial toxin action in disease.Ann Intern Med. 1984 Nov;101(5):653-66. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-5-653. Ann Intern Med. 1984. PMID: 6148909 Review.
-
Pharmacologic action of Escherichia coli heat-stable (STa) enterotoxin.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 1992 Sep;28(2):67-72. doi: 10.1016/1056-8719(92)90049-7. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 1992. PMID: 1336410 Review.
Cited by
-
Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Enterotoxin Mediates Na+/H+ Exchanger 4 Inhibition Involving cAMP in T84 Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 29;10(12):e0146042. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146042. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26713849 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and design of DNA and RNA ligase inhibitors in infectious microorganisms.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2009 Dec 1;4(12):1281-1294. doi: 10.1517/17460440903373617. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2009. PMID: 20354588 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of styryl-linked fused dihydropyridines by catalyst-free multicomponent reactions.Mol Divers. 2021 Nov;25(4):2161-2169. doi: 10.1007/s11030-021-10216-4. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Mol Divers. 2021. PMID: 33860877
-
Toxin mediated diarrhea in the 21 century: the pathophysiology of intestinal ion transport in the course of ETEC, V. cholerae and rotavirus infection.Toxins (Basel). 2010 Aug;2(8):2132-57. doi: 10.3390/toxins2082132. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of novel 7-aryl and 7-spiropyrazolo[4',3':5,6]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives and their study as AChE inhibitors.Mol Divers. 2017 Nov;21(4):943-955. doi: 10.1007/s11030-017-9774-3. Epub 2017 Aug 7. Mol Divers. 2017. PMID: 28785929
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

