'Linkage analysis of thyroid antibody production: evidence for shared susceptibility to clinical autoimmune thyroid disease
- PMID: 18559906
- PMCID: PMC2567858
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2008-0364
'Linkage analysis of thyroid antibody production: evidence for shared susceptibility to clinical autoimmune thyroid disease
Abstract
Context: Epidemiological data suggest a genetic susceptibility to thyroid antibody (TAb) production.
Objective: The objective of the study was to identify genetic loci that are linked with TAb production.
Design: The design of the study was a whole genome linkage study in families with clustering of thyroid autoimmunity.
Settings: The study took place at an academic medical center.
Participants: Participants included 102 multigenerational families (540 individuals) multiplex for autoimmune thyroid disease (AITD) and TAb production.
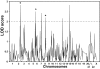
Main outcome measures: We computed two-point logarithm of odds (LOD) scores and multipoint heterogeneity LOD scores for 400 microsatellite markers spanning the entire human genome at an average distance of 10 cm (approximately 10 Mb).
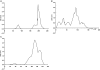
Results: Three loci showed evidence for linkage with TAb production: 1) 2q locus, which gave a maximum multipoint heterogeneity LOD score (HLOD) of 2.8 and contained the CTLA-4 gene, previously reported to be linked and associated with clinical AITD; (2) 6p locus (HLOD 2.5), which was the same AITD-1 locus found to be linked with clinical AITD; and (3) 8q locus (HLOD 2.2), which contained the thyroglobulin gene, also previously reported to be linked and associated with AITD. All loci that were linked to TAb were also linked to AITD, suggesting that TAb and AITD share the same genetic predisposition.
Conclusions: We conclude that: 1) some of the genes/loci predisposing to TAb and AITD are shared, whereas distinct genes/loci also exist; (2) the presence of TAb in relatives of AITD patients may be associated with increased risk for the development of clinical AITD; and (3) further studies are needed to determine the predictive value of TAb levels for the development of clinical AITD in relatives of patients with familial AITD.
Figures
References
-
- Davies TF 2000 Graves’ diseases: pathogenesis. In: Braverman LE, Utiger RD, eds. Werner and Ingbar’s the thyroid: a fundamental and clinical text. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 518–530
-
- Weetman AP 2000 Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. In: Braverman LE, Utiger RD, eds. Werner and Ingbar’s the thyroid. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 721–732
-
- Jacobson DL, Gange SJ, Rose NR, Graham NM 1997 Epidemiology and estimated population burden of selected autoimmune diseases in the United States. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 84:223–243 - PubMed
-
- Hollowell JG, Staehling NW, Flanders WD, Hannon WH, Gunter EW, Spencer CA, Braverman LE 2002 Serum TSH, T(4), and thyroid antibodies in the United States population (1988 to 1994): National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:489–499 - PubMed
-
- Vanderpump MPJ, Tunbridge WMG, French JM, Appleton D, Bates D, Clark F, Grimley Evans J, Hasan DM, Rodgers H, Tunbridge F, Young ET 1995 The incidence of thyroid disorders in the community: a twenty-year follow-up of the Whickham survey. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 43:55–68 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK067555/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073681/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK61659/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067555/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK31775/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH048858/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS027941/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052464/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- NS27941/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK031775/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK061659/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK073681/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MH48858/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DK052464/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

