Absence of SKP2 expression attenuates BCR-ABL-induced myeloproliferative disease
- PMID: 18559973
- PMCID: PMC2518897
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-113860
Absence of SKP2 expression attenuates BCR-ABL-induced myeloproliferative disease
Abstract
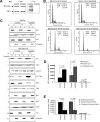
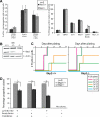
BCR-ABL is proposed to impair cell-cycle control by disabling p27, a tumor suppressor that inhibits cyclin-dependent kinases. We show that in cell lines p27 expression is inversely correlated with expression of SKP2, the F-box protein of SCF(SKP2) (SKP1/Cul1/F-box), the E3 ubiquitin ligase that promotes proteasomal degradation of p27. Inhibition of BCR-ABL kinase causes G(1) arrest, down-regulation of SKP2, and accumulation of p27. Ectopic expression of wild-type SKP2, but not a mutant unable to recognize p27, partially rescues cell-cycle progression. A similar regulation pattern is seen in cell lines transformed by FLT3-ITD, JAK2(V617F), and TEL-PDGFRbeta, suggesting that the SKP2/p27 conduit may be a universal target for leukemogenic tyrosine kinases. Mice that received transplants of BCR-ABL-infected SKP2(-/-) marrow developed a myeloproliferative syndrome but survival was significantly prolonged compared with recipients of BCR-ABL-expressing SKP2(+/+) marrow. SKP2(-/-) leukemic cells demonstrated higher levels of nuclear p27 than SKP2(+/+) counterparts, suggesting that the attenuation of leukemogenesis depends on increased p27 expression. Our data identify SKP2 as a crucial mediator of BCR-ABL-induced leukemogenesis and provide the first in vivo evidence that SKP2 promotes oncogenesis. Hence, stabilization of p27 by inhibiting its recognition by SCF(SKP2) may be therapeutically useful.
Figures





References
-
- Deininger MW, Goldman JM, Melo JV. The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2000;96:3343–3356. - PubMed
-
- Clarkson B, Strife A, Wisniewski D, Lambek CL, Liu C. Chronic myelogenous leukemia as a paradigm of early cancer and possible curative strategies. Leukemia. 2003;17:1211–1262. - PubMed
-
- Attar EC, Scadden DT. Regulation of hematopoietic stem cell growth. Leukemia. 2004;18:1760–1768. - PubMed
-
- Skorski T, Kanakaraj P, Nieborowska-Skorska M, et al. Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase activity is regulated by BCR/ABL and is required for the growth of Philadelphia chromosome-positive cells. Blood. 1995;86:726–736. - PubMed
-
- Cortez D, Reuther G, Pendergast AM. The Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase activates mitogenic signaling pathways and stimulates G1-to-S phase transition in hematopoietic cells. Oncogene. 1997;15:2333–2342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

