Polychlorinated biphenyl-77 induces adipocyte differentiation and proinflammatory adipokines and promotes obesity and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 18560532
- PMCID: PMC2430232
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.10554
Polychlorinated biphenyl-77 induces adipocyte differentiation and proinflammatory adipokines and promotes obesity and atherosclerosis
Abstract
Background: Obesity, an inflammatory condition linked to cardiovascular disease, is associated with expansion of adipose tissue. Highly prevalent coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) such as 3,3',4,4'-tetrachlorobiphenyl (PCB-77) accumulate in adipose tissue because of their lipophilicity and increase with obesity. However, the effects of PCBs on adipocytes, obesity, and obesity-associated cardiovascular disease are unknown.
Objectives: In this study we examined in vitro and in vivo effects of PCB-77 on adipocyte differentiation, proinflammatory adipokines, adipocyte morphology, body weight, serum lipids, and atherosclerosis.
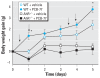
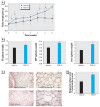
Methods: PCB-77 or 2,2',4,4,5,5'-hexachlorobiphenyl (PCB-153) was incubated with 3T3-L1 adipocytes either during differentiation or in mature adipocytes. Concentration-dependent effects of PCB-77 were contrasted with those of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). For in vivo studies, we treated C57BL/6 wild-type (WT) or aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)(-/-) mice with vehicle or PCB-77 (49 mg/kg, by intraperitoneal injection) and examined body weight gain. In separate studies, we injected ApoE(-/-) mice with vehicle or PCB-77 over a 6-week period and examined body weight, adipocyte size, serum lipids, and atherosclerosis.
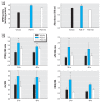
Results: Low concentrations of PCB-77 or TCDD increased adipocyte differentiation, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity, and expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, whereas higher concentrations inhibited adipocyte differentiation. Effects of PCB-77 were abolished by the AhR antagonist alpha-naphthoflavone. PCB-77 promoted the expression and release of various proinflammatory cytokines from 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Administration of PCB-77 increased body weight gain in WT but not AhR(-/-) mice. ApoE(-/-) mice injected with PCB-77 exhibited greater body weight, adipocyte hypertrophy, serum dyslipidemia, and augmented atherosclerosis.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that PCB-77 may contribute to the development of obesity and obesity-associated atherosclerosis.
Keywords: adipocyte differentiation; aryl hydrocarbon receptor; ectopic lipid deposition; obesity; polychlorinated biphenyl.
Figures



References
-
- Alexander DL, Ganem LG, Fernandez-Salguero P, Gonzalez F, Jefcoate CR. Aryl-hydrocarbon receptor is an inhibitory regulator of lipid synthesis and of commitment to adipogenesis. J Cell Sci. 1998;111(Pt 22):3311–3322. - PubMed
-
- Bertazzi PA, Zocchetti C, Guercilena S, Consonni D, Tironi A, Landi MT, et al. Dioxin exposure and cancer risk: a 15-year mortality study after the “Seveso accident. Epidemiology. 1997;8:646–652. - PubMed
-
- Brodie AE, Azarenko VA, Hu CY. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) inhibition of fat cell differentiation. Toxicol Lett. 1996;84:55–59. - PubMed
-
- Brodie AE, Azarenko VA, Hu CY. Inhibition of increases of transcription factor mRNAs during differentiation of primary rat adipocytes by in vivo 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) treatment. Toxicol Lett. 1997;90:91–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
