Suppression of tumor growth and angiogenesis by a specific antagonist of the cell-surface expressed nucleolin
- PMID: 18560571
- PMCID: PMC2424174
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002518
Suppression of tumor growth and angiogenesis by a specific antagonist of the cell-surface expressed nucleolin
Abstract
Background: Emerging evidences suggest that nucleolin expressed on the cell surface is implicated in growth of tumor cells and angiogenesis. Nucleolin is one of the major proteins of the nucleolus, but it is also expressed on the cell surface where is serves as a binding protein for variety of ligands implicated in cell proliferation, differentiation, adhesion, mitogenesis and angiogenesis.
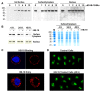
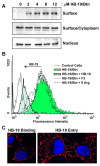
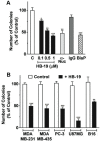
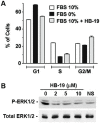
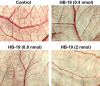
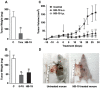
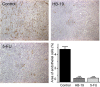
Methodology/principal findings: By using a specific antagonist that binds the C-terminal tail of nucleolin, the HB-19 pseudopeptide, here we show that the growth of tumor cells and angiogenesis are suppressed in various in vitro and in vivo experimental models. HB-19 inhibited colony formation in soft agar of tumor cell lines, impaired migration of endothelial cells and formation of capillary-like structures in collagen gel, and reduced blood vessel branching in the chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane. In athymic nude mice, HB-19 treatment markedly suppressed the progression of established human breast tumor cell xenografts in nude mice, and in some cases eliminated measurable tumors while displaying no toxicity to normal tissue. This potent antitumoral effect is attributed to the direct inhibitory action of HB-19 on both tumor and endothelial cells by blocking and down regulating surface nucleolin, but without any apparent effect on nucleolar nucleolin.
Conclusion/significance: Our results illustrate the dual inhibitory action of HB-19 on the tumor development and the neovascularization process, thus validating the cell-surface expressed nucleolin as a strategic target for an effective cancer drug. Consequently, the HB-19 pseudopeptide provides a unique candidate to consider for innovative cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeting surface nucleolin with multivalent HB-19 and related Nucant pseudopeptides results in distinct inhibitory mechanisms depending on the malignant tumor cell type.BMC Cancer. 2011 Aug 3;11:333. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-333. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21812966 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting surface nucleolin with a multivalent pseudopeptide delays development of spontaneous melanoma in RET transgenic mice.BMC Cancer. 2010 Jun 24;10:325. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-325. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20573279 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of tumorigenicity of rhabdoid tumor derived G401 cells by the multivalent HB-19 pseudopeptide that targets surface nucleolin.Biochimie. 2011 Mar;93(3):426-33. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.10.015. Epub 2010 Oct 30. Biochimie. 2011. PMID: 21040752
-
Midkine, a cytokine that inhibits HIV infection by binding to the cell surface expressed nucleolin.Cell Res. 2006 Feb;16(2):174-81. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310024. Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16474431 Review.
-
Cell surface nucleolin as active bait for nanomedicine in cancer therapy: a promising option.Nanotechnology. 2021 May 17;32(32). doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/abfb30. Nanotechnology. 2021. PMID: 33892482 Review.
Cited by
-
Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Carriers for DOX and Magnetic Hyperthermia after Intratumoral Application into Breast Cancer in Mice: Impact and Future Perspectives.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 May 26;10(6):1016. doi: 10.3390/nano10061016. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32466552 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Nanoparticles in Cancer Theranostics.Theranostics. 2015 Sep 1;5(11):1249-63. doi: 10.7150/thno.11544. eCollection 2015. Theranostics. 2015. PMID: 26379790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of nucleolin. Focus on cancer and anti-cancer therapy.Saudi Med J. 2016 Dec;37(12):1312-1318. doi: 10.15537/smj.2016.12.15972. Saudi Med J. 2016. PMID: 27874146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel fully human anti-NCL immunoRNase for triple-negative breast cancer therapy.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 27;7(52):87016-87030. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13522. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27894092 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of the combined score of endothelial expression of nucleolin and CD31 in surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54674. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054674. Epub 2013 Jan 31. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23382938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Srivastava M, Pollard HB. Molecular dissection of nucleolin's role in growth and cell proliferation: new insights. FASEB J. 1999;13:1911–1922. - PubMed
-
- Storck S, Shukla M, Dimitrov S, Bouvet P. Functions of the histone chaperone nucleolin in diseases. Subcell Biochem. 2007;41 - PubMed
-
- Hovanessian AG, Puvion-Dutilleul F, Nisole S, Svab J, Perret E, et al. The cell-surface-expressed nucleolin is associated with the actin cytoskeleton. Exp Cell Res. 2000;261:312–328. - PubMed
-
- Carpentier M, Morelle W, Coddeville B, Pons A, Masson M, et al. Nucleolin undergoes partial N- and O-glycosylations in the extranuclear cell compartment. Biochemisty. 2005;44:5804–5814. - PubMed
-
- Semenkovich CF, Ostlund REJ, Olson MO, Yang JW. A protein partially expressed on the surface of HepG2 cells that binds lipoproteins specifically is nucleolin. Biochemistry. 1990;29:9708–9713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

