Functional modes of the regulatory arm of AraC
- PMID: 18561170
- PMCID: PMC2605204
- DOI: 10.1002/prot.22137
Functional modes of the regulatory arm of AraC
Abstract
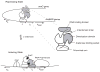
One of the two crystal structures of the arm-dimerization domain determined in the absence of arbinose fails to show the arm, whereas the other structure does show it. The two structures lead to different pictures for the regulatory behavior of the arms. Trypsin digestion, fluorescence anisotropy, and NMR experiments presented here were designed to resolve the issue and show that in arm-dimerization domain, the arms are structured, although differently, in the presence and absence of arabinose. The arms have also been shown to interact with the DNA binding domains of AraC by their requirement for the immobilization of the DNA binding domains that is necessary for DNA looping and repression. The binding of arabinose has been shown to release the DNA binding domains and looping ceases. The picture resulting from the new experiments and the crystal structures of the arm-dimerization domain is that in the absence of arabinose, the arm adopts one structure on the dimerization domain and that the DNA binding domain then binds to this complex. Upon binding arabinose, the arm restructures and as a result, no longer serves as a gasket between the DNA binding domain and dimerization domain. The DNA binding domain is then released, subject only to the constraints imposed by the flexible linker connecting it to dimerization domain, and the protein relocates on the DNA and activates transcription.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Arabinose Alters Both Local and Distal H-D Exchange Rates in the Escherichia coli AraC Transcriptional Regulator.Biochemistry. 2019 Jul 2;58(26):2875-2882. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00389. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31199144 Free PMC article.
-
A genetic and physical study of the interdomain linker of E. Coli AraC protein--a trans-subunit communication pathway.Proteins. 2016 Apr;84(4):448-60. doi: 10.1002/prot.24990. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Proteins. 2016. PMID: 26800223
-
A new and unexpected domain-domain interaction in the AraC protein.Proteins. 2012 May;80(5):1465-75. doi: 10.1002/prot.24044. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Proteins. 2012. PMID: 22383259
-
AraC protein, regulation of the l-arabinose operon in Escherichia coli, and the light switch mechanism of AraC action.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010 Sep;34(5):779-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00226.x. Epub 2010 Apr 8. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20491933 Review.
-
AraC protein: a love-hate relationship.Bioessays. 2003 Mar;25(3):274-82. doi: 10.1002/bies.10237. Bioessays. 2003. PMID: 12596232 Review.
Cited by
-
Elucidating residue roles in engineered variants of AraC regulatory protein.Protein Sci. 2010 Feb;19(2):291-8. doi: 10.1002/pro.310. Protein Sci. 2010. PMID: 20014443 Free PMC article.
-
Arabinose Alters Both Local and Distal H-D Exchange Rates in the Escherichia coli AraC Transcriptional Regulator.Biochemistry. 2019 Jul 2;58(26):2875-2882. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00389. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31199144 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence regulons of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Immunol Res. 2013 Dec;57(1-3):229-36. doi: 10.1007/s12026-013-8453-4. Immunol Res. 2013. PMID: 24203442 Review.
-
Unexpected coregulator range for the global regulator Lrp of Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis.J Bacteriol. 2011 Mar;193(5):1054-64. doi: 10.1128/JB.01183-10. Epub 2010 Dec 17. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21169483 Free PMC article.
-
Computational predictions of the mutant behavior of AraC.J Mol Biol. 2010 May 7;398(3):462-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.03.021. Epub 2010 Mar 23. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20338183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saviola B, Seabold R, Schleif R. Arm-domain interactions in AraC. J Mol Biol. 1998;278:539–548. - PubMed
-
- Seabold R, Schleif R. Apo-AraC actively seeks to loop. J Mol Biol. 1998;278:529–538. - PubMed
-
- Reed W, Schleif R. Hemiplegic mutations in AraC protein. J Mol Biol. 1999;294:417–425. - PubMed
-
- Ross J, Gryczynski U, Schleif R. Mutational analysis of residue roles in AraC function. J Mol Biol. 2003;328:85–93. - PubMed
-
- Soisson S, MacDougal-Shackleton B, Schleif R, Wolberger C. Structural basis for ligand-regulated oligomerization of AraC. Science. 1997;276:421–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

