Novel combination treatment of type 2 diabetes DPP-4 inhibition + metformin
- PMID: 18561513
- PMCID: PMC2496991
- DOI: 10.2147/vhrm.s1944
Novel combination treatment of type 2 diabetes DPP-4 inhibition + metformin
Abstract
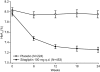
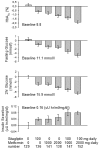
Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) as a novel therapy for type 2 diabetes is based on prevention of the inactivation process of bioactive peptides, the most important in the context of treatment of diabetes of which is glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). Most clinical experience with DPP-4 inhibition is based on vildagliptin (GalvusR, Novartis) and sitagliptin (JanuviaR, Merck). These compounds improve glycemic control both in monotherapy and in combination with other oral hyperglycemic agents. Both have also been shown to efficiently improve glycemic control when added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with inadequate glycemic control. Under that condition, they reduce HbA1C levels by 0.65%-1.1% (baseline HbA1C 7.2-8.7%) in studies up to 52 weeks of duration in combination versus continuous therapy with metformin alone. Sitagliptin has also been examined in initial combination therapy with metformin have; HbA1 was reduced by this combination by 2.1% (baseline HbA1C 8.8%) after 24 weeks of treatment. Both fasting and prandial glucose are reduced by DPP-4 inhibition in combination with metformin in association with improvement of insulin secretion and insulin resistance and increase in concentrations of active GLP-1. The combination of DPP-4 inhibition and metformin has been shown to be highly tolerable with very low risk of hypoglycemia. Hence, DPP-4 inhibition in combination with metformin is an efficient, safe and tolerable combination therapy for type 2 diabetes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Clinical results of treating type 2 diabetic patients with sitagliptin, vildagliptin or saxagliptin--diabetes control and potential adverse events.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Aug;23(4):487-98. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2009.03.003. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19748066 Review.
-
Combination therapy with DPP-4 inhibitors and pioglitazone in type 2 diabetes: theoretical consideration and therapeutic potential.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008;4(6):1221-7. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.s3374. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008. PMID: 19337535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incretin mimetics and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in clinical trials for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008 Jun;17(6):845-53. doi: 10.1517/13543784.17.6.845. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18491986 Review.
-
DPP-4 inhibitors.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Dec;21(4):517-33. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2007.07.005. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 18054733 Review.
-
GLP-1-based therapy of type 2 diabetes: GLP-1 mimetics and DPP-IV inhibitors.Curr Diab Rep. 2007 Oct;7(5):340-7. doi: 10.1007/s11892-007-0056-9. Curr Diab Rep. 2007. PMID: 18173966 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of the combination of metformin and fenofibrate on glucose homeostasis in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats.Exp Mol Med. 2013 Jul 5;45(7):e30. doi: 10.1038/emm.2013.58. Exp Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23827952 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of insulin with incretin therapies for management of type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Ther. 2011 Sep;2(3):146-61. doi: 10.1007/s13300-011-0005-0. Epub 2011 Jul 21. Diabetes Ther. 2011. PMID: 22127824 Free PMC article.
-
DPP-4 Inhibition and the Path to Clinical Proof.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Jun 19;10:376. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00376. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31275243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vildagliptin vs sulfonylurea in Indian Muslim diabetes patients fasting during Ramadan.World J Diabetes. 2013 Dec 15;4(6):358-64. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v4.i6.358. World J Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 24379927 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of metformin monotherapy and dual or triple concomitant therapy with metformin on glycemic control and lipid profile management of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 14;9:995944. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.995944. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36314019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahrén B. Vildagliptin: an inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 with antidiabetic properties. Exp Opin Invest Drugs. 2006;15:431–42. - PubMed
-
- Ahrén B. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors – clinical data and clinical implications. Diabetes Care. 2007a;30:1344–50. - PubMed
-
- Ahrén B. DPP-4 inhibitors. In: Barnett A, Bailey C, editors. Best practice and research: clinical endocrinology and metabolism; novel therapies of diabetes. 2007b. - PubMed
-
- Ahrén B, Pacini G. Impaired adaptation of first-phase insulin secretion in postmenopausal women with glucose tolerance. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:E701–7. - PubMed
-
- Ahrén B, Simonsson E, Larsson H, et al. Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV improves metabolic control over a 4 week study period in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:869–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

