Lipoic acid stimulates cAMP production via the EP2 and EP4 prostanoid receptors and inhibits IFN gamma synthesis and cellular cytotoxicity in NK cells
- PMID: 18562016
- PMCID: PMC2561179
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.05.003
Lipoic acid stimulates cAMP production via the EP2 and EP4 prostanoid receptors and inhibits IFN gamma synthesis and cellular cytotoxicity in NK cells
Abstract
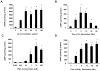
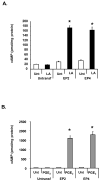
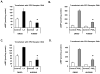
The antioxidant lipoic acid (LA) treats and prevents the animal model of multiple sclerosis (MS), experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). In an effort to understand the therapeutic potential of LA in MS, we sought to define the cellular mechanisms that mediate the effects of LA on human natural killer (NK) cells, which are important in innate immunity as the first line of defense against invading pathogens and tumor cells. We discovered that LA stimulates cAMP production in NK cells in a dose-dependent manner. Studies using pharmacological inhibitors and receptor transfection experiments indicate that LA stimulates cAMP production via activation of the EP2 and EP4 prostanoid receptors and adenylyl cyclase. In addition, LA suppressed interleukin (IL)-12/IL-18 induced IFNgamma secretion and cytotoxicity in NK cells. These novel findings suggest that LA may inhibit NK cell function via the cAMP signaling pathway.
Figures
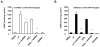
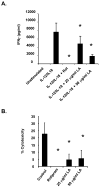
References
-
- Anderson KA, Ribar TJ, Illario M, Means AR. Defective survival and activation of thymocytes in transgenic mice expressing a catalytically inactive form of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV. Mol Endocrinol. 1997;11:725–737. - PubMed
-
- Antel JP, McCrea E, Ladiwala U, Qin YF, Becher B. Non-MHC-restricted cell-mediated lysis of human oligodendrocytes in vitro: relation with CD56 expression. J Immunol. 1998;160:1606–1611. - PubMed
-
- Aranami T, Miyake S, Yamamura T. Differential expression of CD11c by peripheral blood NK cells reflects temporal activity of multiple sclerosis. J Immunol. 2006;177:5659–5667. - PubMed
-
- Artwohl M, Muth K, Kosulin K, de Martin R, Holzenbein T, Rainer G, Freudenthaler A, Huttary N, Schmetterer L, Waldhausl WK, Baumgartner-Parzer SM. R-(+)-alpha-lipoic acid inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis and proliferation: involvement of Akt and retinoblastoma protein/E2F-1. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;293:E681–689. - PubMed
-
- Bariagaber AK, Whalen MM. Decreased adenylyl cyclase and cAMP-dependent protein kinase activities inhibit the cytotoxic function of human natural killer cells. Hum Immunol. 2003;64:866–873. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

