Cross-sectional multicenter study of patients with urea cycle disorders in the United States
- PMID: 18562231
- PMCID: PMC2640937
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2008.05.004
Cross-sectional multicenter study of patients with urea cycle disorders in the United States
Abstract
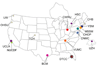
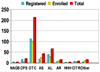
Inherited urea cycle disorders comprise eight disorders (UCD), each caused by a deficiency of one of the proteins that is essential for ureagenesis. We report on a cross-sectional investigation to determine clinical and laboratory characteristics of patients with UCD in the United States. The data used for the analysis was collected at the time of enrollment of individuals with inherited UCD into a longitudinal observation study. The study has been conducted by the Urea Cycle Disorders Consortium within the Rare Diseases Clinical Research Network (RDCRN) funded by the National Institutes of Health. One-hundred eighty-three patients were enrolled into the study. Ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency was the most frequent disorder (55%), followed by argininosuccinic aciduria (16%) and citrullinemia (14%). Seventy-nine percent of the participants were white (16% Latinos), and 6% were African American. Intellectual and developmental disabilities were reported in 39% with learning disabilities (35%) and half had abnormal neurological examination. Sixty-three percent were on a protein restricted diet, 37% were on Na-phenylbutyrate and 5% were on Na-benzoate. Forty-five percent of OTC deficient patients were on L-citrulline, while most patients with citrullinemia (58%) and argininosuccinic aciduria (79%) were on L-arginine. Plasma levels of branched-chain amino acids were reduced in patients treated with ammonia scavenger drugs. Plasma glutamine levels were higher in proximal UCD and in neonatal type disease. The RDCRN allows comprehensive analyses of rare inherited UCD, their frequencies and current medical practices.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hereditary urea cycle diseases in Finland.Acta Paediatr. 2008 Oct;97(10):1412-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.2008.00923.x. Epub 2008 Jul 9. Acta Paediatr. 2008. PMID: 18616627
-
Evaluation of dietary treatment and amino acid supplementation in organic acidurias and urea-cycle disorders: On the basis of information from a European multicenter registry.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2019 Nov;42(6):1162-1175. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12066. Epub 2019 Feb 27. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2019. PMID: 30734935
-
Diagnosis, symptoms, frequency and mortality of 260 patients with urea cycle disorders from a 21-year, multicentre study of acute hyperammonaemic episodes.Acta Paediatr. 2008 Oct;97(10):1420-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.2008.00952.x. Epub 2008 Jul 17. Acta Paediatr. 2008. PMID: 18647279 Free PMC article.
-
Urea cycle disorders: clinical presentation outside the newborn period.Crit Care Clin. 2005 Oct;21(4 Suppl):S9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2005.05.007. Crit Care Clin. 2005. PMID: 16227115 Review.
-
[Disorders of the urea cycle].Ryoikibetsu Shokogun Shirizu. 2000;(29 Pt 4):390-2. Ryoikibetsu Shokogun Shirizu. 2000. PMID: 11031978 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Rescue Treatment with L-Citrulline Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Newborn Pigs.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015 Aug;53(2):255-64. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0351OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25536367 Free PMC article.
-
Can psychiatric childhood disorders be due to inborn errors of metabolism?Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017 Feb;26(2):143-154. doi: 10.1007/s00787-016-0908-4. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 27695954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between longitudinal changes in neuropsychological outcome and disease biomarkers in urea cycle disorders.Pediatr Res. 2023 Dec;94(6):2005-2015. doi: 10.1038/s41390-023-02722-y. Epub 2023 Jul 15. Pediatr Res. 2023. PMID: 37454183
-
Argininosuccinate lyase deficiency: longterm outcome of 13 patients detected by newborn screening.Mol Genet Metab. 2009 Nov;98(3):273-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.06.011. Epub 2009 Jun 25. Mol Genet Metab. 2009. PMID: 19635676 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a single dose of N-carbamylglutamate on the rate of ureagenesis.Mol Genet Metab. 2009 Dec;98(4):325-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.07.010. Epub 2009 Jul 14. Mol Genet Metab. 2009. PMID: 19660971 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Rare Diseases Act of 2002 Public Law 107–280 107th Congress. HOUSE Reports: No. 107–543 (Committee on Energy and Commerce). Senate Reports: No. 107–129 accompanying S. 1379 (Comm. on Health)
-
- McCullough BA, Yudkoff M, Batshaw ML, Wilson JM, Raper SE, Tuchman M. Genotype spectrum of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency: Correlation with the clinical and biochemical phenotype. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000;93:313–319. - PubMed
-
- Progress against childhood cancer: the Pediatric Oncology Group experience. Pediatr. 1992;89(4 Pt 1):597–600. [No authors listed] - PubMed
-
- Richesson RL, Lee HS, Cuthbertson D, Lloyd J, Young K, Krischer JP. An automated communication system in a contact registry for persons with rare diseases: scalable tools for identifying and recruiting clinical research participants. submitted to Methods of Information in Medicine, Feb 2008. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nagata N, Matsuda I, Oyanagi K. Estimated frequency of urea cycle enzymopathies in Japan. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1991;39:228–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

