A long helix from the central region of smooth muscle caldesmon
- PMID: 1856225
- PMCID: PMC1262681
A long helix from the central region of smooth muscle caldesmon
Abstract
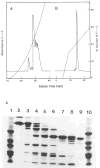
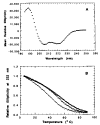
The central region of smooth muscle caldesmon is predicted to form alpha-helices on the basis of its primary structure. We have isolated a fragment (CT54) that contains this region. The hydrodynamic properties and the electron microscopic images suggest that CT54 is an elongated (35 nm), monomeric molecule. The circular dichroic spectrum yields an overall alpha-helical content of 55-58%. These results are consistent with the model that the middle portion of CT54 forms a long stretch of single-stranded alpha-helix. Such a structure, if it in fact exists, is thought to be stabilized by numerous salt bridges between charged residues at positions i and i + 4. The structural characteristics of this fragment not only represent an unusual protein configuration but also provide information about the functional role of caldesmon in smooth muscle contraction.
Figures




Similar articles
-
(i, i + 4) Ion pairs stabilize helical peptides derived from smooth muscle caldesmon.Arch Biochem Biophys. 1996 May 15;329(2):156-62. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1996.0204. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1996. PMID: 8638947
-
Conformational change of turkey-gizzard caldesmon induced by specific chemical modification with carbodiimide.Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jan 30;195(2):335-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15711.x. Eur J Biochem. 1991. PMID: 1997319
-
Phosphatidylserine liposomes can be tethered by caldesmon to actin filaments.Biophys J. 1997 Sep;73(3):1607-16. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78192-X. Biophys J. 1997. PMID: 9284327 Free PMC article.
-
Caldesmon: fragments, sequence, and domain mapping.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;599:100-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42368.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990. PMID: 2221667 Review.
-
Structural interactions between actin, tropomyosin, caldesmon and calcium binding protein and the regulation of smooth muscle thin filaments.Acta Physiol Scand. 1998 Dec;164(4):401-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-201x.1998.tb10696.x. Acta Physiol Scand. 1998. PMID: 9887964 Review.
Cited by
-
Smooth muscle caldesmon modulates peristalsis in the wild type and non-innervated zebrafish intestine.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012 Mar;24(3):288-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2011.01844.x. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012. PMID: 22316291 Free PMC article.
-
Disulphide cross-linking of smooth-muscle and non-muscle caldesmon to the C-terminus of actin in reconstituted and native thin filaments.Biochem J. 1993 Aug 15;294 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):63-7. doi: 10.1042/bj2940063. Biochem J. 1993. PMID: 8363587 Free PMC article.
-
Flexation of caldesmon: effect of conformation on the properties of caldesmon.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1995 Oct;16(5):509-18. doi: 10.1007/BF00126435. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1995. PMID: 8567938
-
Distribution and evolution of stable single α-helices (SAH domains) in myosin motor proteins.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 3;12(4):e0174639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174639. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28369123 Free PMC article.
-
Caldesmon and the regulation of cytoskeletal functions.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;644:250-72. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-85766-4_19. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 19209827 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

