Reciprocal patterns of methylation of H3K36 and H3K27 on proximal vs. distal IgVH genes are modulated by IL-7 and Pax5
- PMID: 18562282
- PMCID: PMC2438410
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0711758105
Reciprocal patterns of methylation of H3K36 and H3K27 on proximal vs. distal IgVH genes are modulated by IL-7 and Pax5
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Dec 16;105(50):20044
Abstract
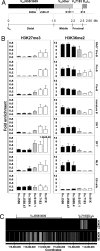
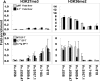
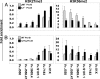
The usage of >100 functional murine Ig heavy chain V(H) genes, when rearranged to D(H)J(H) genes, generates a diverse antibody repertoire. The V(H) locus encompasses 2.5 Mb, and rearrangement of V(H) genes in the D(H)-distal half of the locus are controlled very differently from the V(H) genes in the proximal end of the locus. The rearrangement of distal but not proximal V(H) genes is impaired in mice deficient in the cytokine IL-7 or its receptor, in the transcription factor Pax5, or in Ezh2, a histone methyltransferase for Lys-27 of histone H3 (H3K27). The relative role of IL-7, Pax5, and Ezh2 in regulating distal vs. proximal V(H) rearrangement is not clear. Here, we show by ChIP and ChIP-on-chip that the active histone modification H3K36me2 is most highly associated with distal V(H) segments and the repressive histone modification H3K27me3 is exclusively present on proximal V(H) segments. We observed an absence of H3K27me3 in fetal pro-B cells, which predominantly rearrange proximal V(H) genes. Absence of IL-7 signaling reduces H3K36me2, and overexpression of IL-7 increases H3K36me2. In contrast, the major effect of the absence of Pax5 is the reduction in H3K27me3. Our data indicate that the cytokine IL-7 and the transcription factor Pax5 influence the rearrangement of the two regions of the V(H) locus by differentially modulating two reciprocal histone modifications during B lymphocyte development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
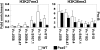
Similar articles
-
Regulation of interleukin 7-dependent immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable gene rearrangements by transcription factor STAT5.Nat Immunol. 2005 Aug;6(8):836-43. doi: 10.1038/ni1226. Epub 2005 Jul 17. Nat Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16025120
-
Pax5 is required for recombination of transcribed, acetylated, 5' IgH V gene segments.Genes Dev. 2003 Jan 1;17(1):37-42. doi: 10.1101/gad.1031403. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 12514097 Free PMC article.
-
Wapl repression by Pax5 promotes V gene recombination by Igh loop extrusion.Nature. 2020 Aug;584(7819):142-147. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2454-y. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32612238 Free PMC article.
-
Pax5: a master regulator of B cell development and leukemogenesis.Adv Immunol. 2011;111:179-206. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385991-4.00005-2. Adv Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21970955 Review.
-
Mechanisms for feedback inhibition of the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus.Curr Opin Immunol. 2004 Apr;16(2):235-40. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2004.02.003. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15023418 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-7 Enables Antibody Responses to Bacterial Polysaccharides by Promoting B Cell Receptor Diversity.J Immunol. 2018 Aug 15;201(4):1229-1240. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800162. Epub 2018 Jul 13. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30006375 Free PMC article.
-
Histone methylation and V(D)J recombination.Int J Hematol. 2014 Sep;100(3):230-7. doi: 10.1007/s12185-014-1637-4. Epub 2014 Jul 25. Int J Hematol. 2014. PMID: 25060705 Review.
-
DNA double-strand breaks relieve USF-mediated repression of Dβ2 germline transcription in developing thymocytes.J Immunol. 2012 Mar 1;188(5):2266-75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002931. Epub 2012 Jan 27. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22287717 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb group proteins: navigators of lineage pathways led astray in cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2009 Nov;9(11):773-84. doi: 10.1038/nrc2736. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19851313 Review.
-
The SET Domain Is Essential for Metnase Functions in Replication Restart and the 5' End of SS-Overhang Cleavage.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 5;10(10):e0139418. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139418. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26437079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jung D, Giallourakis C, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW. Mechanism and control of V(D)J recombination at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:541–570. - PubMed
-
- Corcoran AE, Riddell A, Krooshoop D, Venkitaraman AR. Impaired immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in mice lacking the IL-7 receptor. Nature. 1998;391:904–907. - PubMed
-
- Su IH, et al. Ezh2 controls B cell development through histone H3 methylation and Igh rearrangement. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:124–131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

