GluR6/KA2 kainate receptors mediate slow-deactivating currents
- PMID: 18562611
- PMCID: PMC6670893
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1204-08.2008
GluR6/KA2 kainate receptors mediate slow-deactivating currents
Abstract
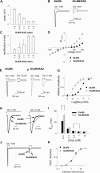
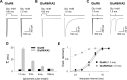
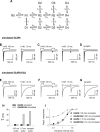
Kainate receptors (KARs) are ionotropic glutamate receptors contributing to EPSCs with a slow-decaying component that is likely essential for synaptic integration. The slow kinetics of KAR-EPSCs markedly contrasts with the fast kinetics reported for recombinant KARs expressed in heterologous systems, for reasons that remain unexplained. Here we have studied the properties of recombinant heteromeric GluR6/KA2 receptors, which compose synaptic KARs. We report that, in response to brief glutamate applications, currents mediated by recombinant GluR6/KA2 receptors, but not GluR6 receptors, decay with a time course similar to KAR-EPSCs. Model simulations suggest that, after brief agonist exposures, GluR6/KA2 currents undergo slow deactivation caused by the stabilization of partially bound open states. We propose, therefore, that the GluR6/KA2 gating features could contribute to the slow KAR-EPSC decay kinetics.
Figures
References
-
- Castillo PE, Malenka RC, Nicoll RA. Kainate receptors mediate a slow postsynaptic current in hippocampal CA3 neurons. Nature. 1997;388:182–186. - PubMed
-
- Cho CH, St-Gelais F, Zhang W, Tomita S, Howe JR. Two families of TARP isoforms that have distinct effects on the kinetic properties of AMPA receptors and synaptic currents. Neuron. 2007;55:890–904. - PubMed
-
- Clements JD, Lester RA, Tong G, Jahr CE, Westbrook GL. The time course of glutamate in the synaptic cleft. Science. 1992;258:1498–1501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
