A dlx2- and pax6-dependent transcriptional code for periglomerular neuron specification in the adult olfactory bulb
- PMID: 18562615
- PMCID: PMC3844782
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0700-08.2008
A dlx2- and pax6-dependent transcriptional code for periglomerular neuron specification in the adult olfactory bulb
Abstract
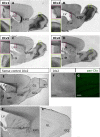
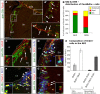
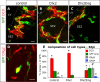
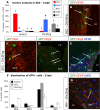
Distinct olfactory bulb (OB) interneurons are thought to become specified depending on from which of the different subregions lining the lateral ventricle wall they originate, but the role of region-specific transcription factors (TFs) in the generation of OB interneurons diversity is still poorly understood. Despite the crucial roles of the Dlx family of TFs for patterning and neurogenesis in the ventral telencephalon during embryonic development, their role in adult neurogenesis has not yet been addressed. Here we show that in the adult brain, Dlx 1 and Dlx2 are expressed in progenitors of the lateral but not the dorsal subependymal zone (SEZ), thus exhibiting a striking regional specificity. Using retroviral vectors to examine the function of Dlx2 in a cell-autonomous manner, we demonstrate that this TF is necessary for neurogenesis of virtually all OB interneurons arising from the lateral SEZ. Beyond its function in generic neurogenesis, Dlx2 also plays a crucial role in neuronal subtype specification in the OB, promoting specification of adult-born periglomerular neurons (PGNs) toward a dopaminergic fate. Strikingly, Dlx2 requires interaction with Pax6, because Pax6 deletion blocks Dlx2-mediated PGN specification. Thus, Dlx2 wields a dual function by first instructing generic neurogenesis from adult precursors and subsequently specifying PGN subtypes in conjunction with Pax6.
Figures


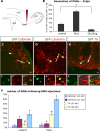
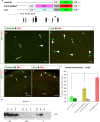
Similar articles
-
Meis2 is a Pax6 co-factor in neurogenesis and dopaminergic periglomerular fate specification in the adult olfactory bulb.Development. 2014 Jan;141(1):28-38. doi: 10.1242/dev.097295. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Development. 2014. PMID: 24284204
-
Pax6 is required for making specific subpopulations of granule and periglomerular neurons in the olfactory bulb.J Neurosci. 2005 Jul 27;25(30):6997-7003. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1435-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16049175 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor Pax6 regulates survival of dopaminergic olfactory bulb neurons via crystallin αA.Neuron. 2010 Nov 18;68(4):682-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.09.030. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 21092858 Free PMC article.
-
Role of a transcription factor Pax6 in the developing vertebrate olfactory system.Dev Growth Differ. 2007 Dec;49(9):683-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2007.00965.x. Epub 2007 Oct 1. Dev Growth Differ. 2007. PMID: 17908181 Review.
-
Concise review: Pax6 transcription factor contributes to both embryonic and adult neurogenesis as a multifunctional regulator.Stem Cells. 2008 Jul;26(7):1663-72. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0884. Epub 2008 May 8. Stem Cells. 2008. PMID: 18467663 Review.
Cited by
-
Plexin-B2 regulates the proliferation and migration of neuroblasts in the postnatal and adult subventricular zone.J Neurosci. 2012 Nov 21;32(47):16892-905. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0344-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23175841 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressor of Fused regulates the proliferation of postnatal neural stem and precursor cells via a Gli3-dependent mechanism.Biol Open. 2019 Jun 6;8(6):bio039248. doi: 10.1242/bio.039248. Biol Open. 2019. PMID: 31142467 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a transient Sox5 expressing progenitor population in the neonatal ventral forebrain by a novel cis-regulatory element.Dev Biol. 2014 Sep 1;393(1):183-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.06.010. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24954155 Free PMC article.
-
PBX1 as Pioneer Factor: A Case Still Open.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Feb 14;5:9. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2017.00009. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28261581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporally Distinct Roles for the Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Sp8 in the Generation and Migration of Dorsal Lateral Ganglionic Eminence (dLGE)-Derived Neuronal Subtypes in the Mouse.Cereb Cortex. 2021 Feb 5;31(3):1744-1762. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaa323. Cereb Cortex. 2021. PMID: 33230547 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen ZJ, II, Waclaw RR, Colbert MC, Campbell K. Molecular identity of olfactory bulb interneurons: transcriptional codes of periglomerular neuron subtypes. J Mol Histol. 2007;38:517–525. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Tramontin AD. A unified hypothesis on the lineage of neural stem cells. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:287–293. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SA, Eisenstat DD, Shi L, Rubenstein JL. Interneuron migration from basal forebrain to neocortex: dependence on Dlx genes. Science. 1997;278:474–476. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SA, Kaznowski CE, Horn C, Rubenstein JL, McConnell SK. Distinct origins of neocortical projection neurons and interneurons in vivo. Cereb Cortex. 2002;12:702–709. - PubMed
-
- Andrews GL, Yun K, Rubenstein JL, Mastick GS. Dlx transcription factors regulate differentiation of dopaminergic neurons of the ventral thalamus. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003;23:107–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
