The chromosomal polymorphism linked to variation in social behavior in the white-throated sparrow (Zonotrichia albicollis) is a complex rearrangement and suppressor of recombination
- PMID: 18562641
- PMCID: PMC2475746
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.108.088229
The chromosomal polymorphism linked to variation in social behavior in the white-throated sparrow (Zonotrichia albicollis) is a complex rearrangement and suppressor of recombination
Abstract
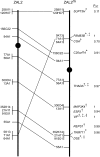
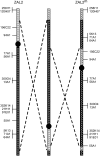
Variation in social behavior and plumage in the white-throated sparrow (Zonotrichia albicollis) is linked to an inversion polymorphism on chromosome 2. Here we report the results of our comparative cytogenetic mapping efforts and population genetics studies focused on the genomic characterization of this balanced chromosomal polymorphism. Comparative chromosome painting and cytogenetic mapping of 15 zebra finch BAC clones to the standard (ZAL2) and alternative (ZAL2(m)) arrangements revealed that this chromosome is orthologous to chicken chromosome 3, and that at a minimum, ZAL2 and ZAL2(m) differ by a pair of included pericentric inversions that we estimate span at least 98 Mb. Population-based sequencing and genotyping of multiple loci demonstrated that ZAL2(m) suppresses recombination in the heterokaryotype and is evolving as a rare nonrecombining autosomal segment of the genome. In addition, we estimate that the first inversion within the ZAL2(m) arrangement originated 2.2+/-0.3 million years ago. Finally, while previously recognized as a genetic model for the evolution of social behavior, we found that the ZAL2/ZAL2(m) polymorphism also shares genetic and phenotypic features with the mouse t complex and we further suggest that the ZAL2/ZAL2(m) polymorphism is a heretofore unrecognized model for the early stages of sex chromosome evolution.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chromosome-wide linkage disequilibrium caused by an inversion polymorphism in the white-throated sparrow (Zonotrichia albicollis).Heredity (Edinb). 2011 Apr;106(4):537-46. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2010.85. Epub 2010 Jun 23. Heredity (Edinb). 2011. PMID: 20571514 Free PMC article.
-
Haplotype-based genomic sequencing of a chromosomal polymorphism in the white-throated sparrow (Zonotrichia albicollis).J Hered. 2011 Jul-Aug;102(4):380-90. doi: 10.1093/jhered/esr043. Epub 2011 May 25. J Hered. 2011. PMID: 21613376 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid regulatory evolution of a nonrecombining autosome linked to divergent behavioral phenotypes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Mar 13;115(11):2794-2799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1717721115. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29483264 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine and genomic architecture of life history trade-offs in an avian model of social behavior.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2008 Jul;157(3):275-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2008.03.023. Epub 2008 Mar 31. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18495122 Review.
-
Supergenes on steroids.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022 Jul 18;377(1855):20200507. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2020.0507. Epub 2022 May 30. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35634926 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chromosomal polymorphism and comparative chromosome painting in the rufous-collared sparrow (Zonotrichia capensis).Genet Mol Biol. 2018 Oct-Dec;41(4):799-805. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2017-0367. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Genet Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30534855 Free PMC article.
-
Iterative evolution of supergene-based social polymorphism in ants.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022 Aug;377(1856):20210196. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0196. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35694755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A candidate chromosome inversion in Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus) identified by population genetic analysis techniques.G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Sep 27;11(10):jkab267. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab267. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 34568922 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of threat response-related polymorphisms at the SLC6A4 locus in callitrichid primates.Biol Lett. 2024 Jul;20(7):20240024. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2024.0024. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39013428 Free PMC article.
-
Wild mice with different social network sizes vary in brain gene expression.BMC Genomics. 2020 Jul 22;21(1):506. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06911-5. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32698762 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bennett, D., 1975. The T-locus of the mouse. Cell 6 441–454.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

