Quantitative trait locus-by-environment interaction for milk yield traits on Bos taurus autosome 6
- PMID: 18562653
- PMCID: PMC2475753
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.107.084483
Quantitative trait locus-by-environment interaction for milk yield traits on Bos taurus autosome 6
Abstract
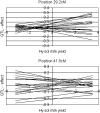
Genotype-by-environment interactions for production traits in dairy cattle have often been observed, while QTL analyses have focused on detecting genes with general effects on production traits. In this study, a QTL search for genes with environmental interaction for the traits milk yield, protein yield, and fat yield were performed on Bos taurus autosome 6 (BTA6), also including information about the previously investigated candidate genes ABCG2 and OPN. The animals in the study were Norwegian Red. Eighteen grandsires and 716 sires were genotyped for 362 markers on BTA6. Every marker bracket was regarded as a putative QTL position. The effects of the candidate genes and the putative QTL were modeled as a regression on an environmental parameter (herd year), which is based on the predicted herd-year effect for the trait. Two QTL were found to have environmentally dependent effects on milk yield. These QTL were located 3.6 cM upstream and 9.1 cM downstream from ABCG2. No environmentally dependent QTL was found to significantly affect protein or fat yield.
Figures
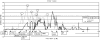
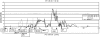

References
-
- Beavis, W. D., 1994. QTL analysis: power, precision and accuracy, pp. 145–162 in Molecular Dissection of Complex Traits, edited by A. H. Paterson. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
-
- Calus, M. P. L., A. F. Groen and G. De Jong, 2002. Genotype × environment interaction for protein yield in Dutch dairy cattle as quantified by different models. J. Dairy Sci. 85 3115–3123. - PubMed
-
- De Jong, G., 1995. Phenotypic plasticity as a product of selection in a variable environment. Am. Nat. 145 493–512. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

