Insights from the amphioxus genome on the origin of vertebrate neural crest
- PMID: 18562679
- PMCID: PMC2493401
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.076208.108
Insights from the amphioxus genome on the origin of vertebrate neural crest
Abstract
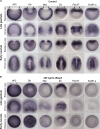
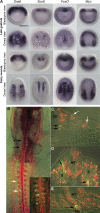
The emergence of the neural crest has been proposed to play a key role in early vertebrate evolution by remodeling the chordate head into a "new head" that enabled early vertebrates to shift from filter feeding to active predation. Here we show that the genome of the basal chordate, amphioxus, contains homologs of most vertebrate genes implicated in a putative neural crest gene regulatory network (NC-GRN) for neural crest development. Our survey of gene expression shows that early inducing signals, neural plate border patterning genes, and melanocyte differentiation genes appear conserved. Furthermore, exogenous BMP affects expression of amphioxus neural plate border genes as in vertebrates, suggesting that conserved signals specify the neural plate border throughout chordates. In contrast to this core conservation, many neural crest specifier genes are not expressed at the amphioxus neural plate/tube border, raising the intriguing possibility that this level of the network was co-opted during vertebrate evolution. Consistent with this, the regulatory region of AmphiFoxD, homologous to the vertebrate neural crest specifier FoxD3, drives tissue-specific reporter expression in chick mesoderm, but not neural crest. Thus, evolution of a new regulatory element may have allowed co-option of this gene to the NC-GRN.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gene duplication, co-option and recruitment during the origin of the vertebrate brain from the invertebrate chordate brain.Brain Behav Evol. 2008;72(2):91-105. doi: 10.1159/000151470. Epub 2008 Oct 7. Brain Behav Evol. 2008. PMID: 18836256 Review.
-
An amphioxus winged helix/forkhead gene, AmphiFoxD: insights into vertebrate neural crest evolution.Dev Dyn. 2002 Nov;225(3):289-97. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.10173. Dev Dyn. 2002. PMID: 12412011
-
The evolutionary origin of the vertebrate neural crest and its developmental gene regulatory network--insights from amphioxus.Zoology (Jena). 2010 Jan;113(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.zool.2009.06.001. Epub 2009 Nov 24. Zoology (Jena). 2010. PMID: 19939657 Review.
-
Conserved RARE localization in amphioxus Hox clusters and implications for Hox code evolution in the vertebrate neural crest.Dev Dyn. 2006 Jun;235(6):1522-31. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20730. Dev Dyn. 2006. PMID: 16538655
-
AmphiPax3/7, an amphioxus paired box gene: insights into chordate myogenesis, neurogenesis, and the possible evolutionary precursor of definitive vertebrate neural crest.Evol Dev. 1999 Nov-Dec;1(3):153-65. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-142x.1999.99019.x. Evol Dev. 1999. PMID: 11324100
Cited by
-
SOXE neofunctionalization and elaboration of the neural crest during chordate evolution.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 13;6:34964. doi: 10.1038/srep34964. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27734831 Free PMC article.
-
Pax3/7 regulates neural tube closure and patterning in a non-vertebrate chordate.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 12;10:999511. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.999511. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36172287 Free PMC article.
-
Phylostratigraphic profiles reveal a deep evolutionary history of the vertebrate head sensory systems.Front Zool. 2013 Apr 12;10(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1742-9994-10-18. Front Zool. 2013. PMID: 23587066 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into neural crest development and evolution from genomic analysis.Genome Res. 2013 Jul;23(7):1069-80. doi: 10.1101/gr.157586.113. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 23817048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network architecture and regulatory logic in neural crest development.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2020 Mar;12(2):e1468. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1468. Epub 2019 Nov 8. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 31702881 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bourlat S.J., Juliusdottir T., Lowe C.J., Freeman R., Aronowicz J., Kirschner M., Lander E.S., Thorndyke M., Nakano H., Kohn A.B., et al. Deuterostome phylogeny reveals monophyletic chordates and the new phylum Xenoturbellida. Nature. 2006;444:85–88. - PubMed
-
- Cheung M., Chaboissier M.C., Mynett A., Hirst E., Schedl A., Briscoe J. The transcriptional control of trunk neural crest induction, survival, and delamination. Dev. Cell. 2005;8:179–192. - PubMed
-
- Conklin E.G. The embryology of amphioxus. J. Morphol. 1932;54:69–151.
-
- Davidson E.H., Erwin D.H. Gene regulatory networks and the evolution of animal body plans. Science. 2006;311:796–800. - PubMed
-
- Denes A.S., Jekely G., Steinmetz P.R., Raible F., Snyman H., Prud'homme B., Ferrier D.E., Balavoine G., Arendt D. Molecular architecture of annelid nerve cord supports common origin of nervous system centralization in bilateria. Cell. 2007;129:277–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
