The Mark Coventry Award: in vivo knee forces during recreation and exercise after knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 18563502
- PMCID: PMC2565055
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-008-0345-x
The Mark Coventry Award: in vivo knee forces during recreation and exercise after knee arthroplasty
Abstract
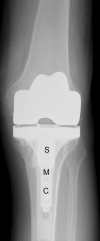
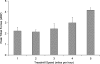
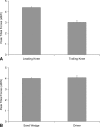
Knee forces directly affect arthroplasty component survivorship, wear of articular bearing surfaces, and integrity of the bone-implant interface. It is not known which activities generate forces within a range that is physiologically desirable but not high enough to jeopardize the survivorship of the prosthetic components. We implanted three patients with an instrumented tibial prosthesis and measured knee forces and moments in vivo during exercise and recreational activities. As expected, stationary bicycling generated low tibial forces, whereas jogging and tennis generated high peak forces. On the other hand, the golf swing generated unexpectedly high forces, especially in the leading knee. Exercise on the elliptical trainer generated lower forces than jogging but not lower than treadmill walking. These novel data allow for a more scientific approach to recommending activities after TKA. In addition, these data can be used to develop clinically relevant structural and tribologic testing, which may result in activity-specific knee designs such as a knee design more tolerant of golfing by optimizing the conflicting needs of increased rotational laxity and conformity.
Figures
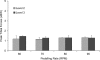


Similar articles
-
Do varus or valgus outliers have higher forces in the medial or lateral compartments than those which are in-range after a kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty? limb and joint line alignment after kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty.Bone Joint J. 2017 Oct;99-B(10):1319-1328. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.99B10.BJJ-2017-0066.R1. Bone Joint J. 2017. PMID: 28963153
-
Three-dimensional knee joint kinematics during golf swing and stationary cycling after total knee arthroplasty.J Orthop Res. 2008 Dec;26(12):1556-61. doi: 10.1002/jor.20671. J Orthop Res. 2008. PMID: 18524002
-
The Mark Coventry Award: Patellofemoral Arthroplasty Results in Better Range of Movement and Early Patient-reported Outcomes Than TKA.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018 Jan;476(1):87-100. doi: 10.1007/s11999.0000000000000017. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018. PMID: 29529622 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Progression of medial osteoarthritis and long term results of lateral unicompartmental arthroplasty: 10 to 18 year follow-up of 54 consecutive implants.Knee. 2014;21 Suppl 1:S26-32. doi: 10.1016/S0968-0160(14)50006-3. Knee. 2014. PMID: 25382364 Review.
-
Is collagen fatigue failure a cause of osteoarthrosis and prosthetic component migration? A hypothesis.J Orthop Res. 1999 Jan;17(1):3-8. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100170103. J Orthop Res. 1999. PMID: 10073641 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Effects of and Response to Mechanical Loading on the Knee.Sports Med. 2022 Feb;52(2):201-235. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01579-7. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 34669175 Review.
-
Knee joint forces: prediction, measurement, and significance.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2012 Feb;226(2):95-102. doi: 10.1177/0954411911433372. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2012. PMID: 22468461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward the interpretation of the combined effect of size and body weight on the tribological performance of total knee prostheses.Int Orthop. 2014 Jun;38(6):1183-90. doi: 10.1007/s00264-014-2297-y. Epub 2014 Feb 26. Int Orthop. 2014. PMID: 24570153 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring Knee Contact Force with Force-Sensing Insoles.Sensors (Basel). 2023 May 19;23(10):4900. doi: 10.3390/s23104900. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37430813 Free PMC article.
-
The cartilage-generated bioelectric potentials induced by dynamic joint movement; an exploratory study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Jul 9;26(1):669. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08939-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40634907 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1152/japplphysiol.00003.2004', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00003.2004'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15258124', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15258124/'}]}
- Biewener AA, Farley CT, Roberts TJ, Temaner M. Muscle mechanical advantage of human walking and running: implications for energy cost. J Appl Physiol. 2004;97:2266–2274. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.jbiomech.2007.03.004', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2007.03.004'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17462659', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17462659/'}]}
- D’Lima DD, Patil S, Steklov N, Chien S, Colwell C Jr. In vivo knee moments and shear after total knee arthroplasty. J Biomech. 2007;40:S11–S17. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/01.blo.0000186559.62942.8c', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/01.blo.0000186559.62942.8c'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16239782', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16239782/'}]}
- D’Lima DD, Patil S, Steklov N, Slamin JE, Colwell CW Jr. The Chitranjan Ranawat Award: in vivo knee forces after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;440:45–49. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.arth.2005.07.011', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2005.07.011'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16520216', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16520216/'}]}
- D’Lima DD, Patil S, Steklov N, Slamin JE, Colwell CW Jr. Tibial forces measured in vivo after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21:255–262. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9111404', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9111404/'}]}
- Diduch DR, Insall JN, Scott WN, Scuderi GR, Font-Rodriguez D. Total knee replacement in young, active patients. Long-term follow-up and functional outcome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79:575–582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

