Polyethylene glycol as a novel resist and sacrificial material for generating positive and negative nanostructures
- PMID: 18563746
- PMCID: PMC8243386
- DOI: 10.1002/smll.200701089
Polyethylene glycol as a novel resist and sacrificial material for generating positive and negative nanostructures
Figures

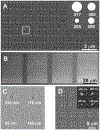


Similar articles
-
Generation of metal photomasks by dip-pen nanolithography.Small. 2009 Aug 17;5(16):1850-3. doi: 10.1002/smll.200801837. Small. 2009. PMID: 19384884 No abstract available.
-
Atomic force microscopy: getting a feeling for the nanoworld.Nat Nanotechnol. 2007 Aug;2(8):461-2. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2007.233. Epub 2007 Jul 29. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007. PMID: 18654337 No abstract available.
-
A nanofountain probe with Sub-100 nm molecular writing resolution.Small. 2005 Jun;1(6):632-5. doi: 10.1002/smll.200500027. Small. 2005. PMID: 17193498 No abstract available.
-
Atomic force microscopy as a multifunctional molecular toolbox in nanobiotechnology.Nat Nanotechnol. 2008 May;3(5):261-9. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2008.100. Nat Nanotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18654521 Review. No abstract available.
-
New approaches to nanofabrication: molding, printing, and other techniques.Chem Rev. 2005 Apr;105(4):1171-96. doi: 10.1021/cr030076o. Chem Rev. 2005. PMID: 15826012 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Inkjet Printed Polyethylene Glycol as a Fugitive Ink for the Fabrication of Flexible Microfluidic Systems.Mater Des. 2018 Jul 15;150:182-187. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.04.013. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Mater Des. 2018. PMID: 30364619 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid lipid membrane coating "shape-locks" silver nanoparticles to prevent surface oxidation and silver ion dissolution.RSC Adv. 2020 Apr 21;10(27):15677-15693. doi: 10.1039/d0ra01727b. eCollection 2020 Apr 21. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35493639 Free PMC article.
-
Silver Nanoparticles Stable to Oxidation and Silver Ion Release Show Size-Dependent Toxicity In Vivo.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Jun 8;11(6):1516. doi: 10.3390/nano11061516. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34201075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Piner RD, Zhu J, Xu F, Hong SH, Mirkin CA, Science 1999, 283, 661–663. - PubMed
-
- Liu X, Guo S, Mirkin CA, Angew. Chem 2003, 115, 4933–4937;
- Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2003, 42, 4785–4789. - PubMed
-
- Jung H, Kulkarni R, Collier CP, J. Am. Chem. Soc 2003, 125, 12096–12097. - PubMed
-
- Sheehan PE, Whitman LJ, King WP, Nelson BA, Appl. Phys. Lett 2004, 85, 1589–1591.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

