Unravelling the bcl-2 apoptosis code with a simple model system
- PMID: 18563968
- PMCID: PMC2429952
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060154
Unravelling the bcl-2 apoptosis code with a simple model system
Abstract
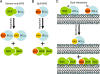
Using defined lipids and purified proteins, Billen et al. offer a new model to reconcile the two currently opposing models for how Bcl-2 family member interactions regulate cell death.
Figures
References
-
- Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ. Cell death: Critical control points. Cell. 2004;116:205–219. - PubMed
-
- Chen WC, Hardwick JM. A quorum on bacterial programmed cell death. Mol Cell. 2007;28:515–517. - PubMed
-
- Youle RJ, Strasser A. The BCL-2 protein family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:47–59. - PubMed
-
- Hetz C, Glimcher L. The daily job of night killers: Alternative roles of the BCL-2 family in organelle physiology. Trends Cell Biol. 2008;18:38–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

