The METEX study: methotrexate versus expectant management in women with ectopic pregnancy: a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 18565217
- PMCID: PMC2453103
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6874-8-10
The METEX study: methotrexate versus expectant management in women with ectopic pregnancy: a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Patients with ectopic pregnancy (EP) and low serum hCG concentrations and women with a pregnancy of unknown location (PUL) and plateauing serum hCG levels are commonly treated with systemic methotrexate (MTX). However, there is no evidence that treatment in these particular subgroups of women is necessary as many of these early EPs may resolve spontaneously. The aim of this study is whether expectant management in women with EP or PUL and with low but plateauing serum hCG concentrations is an alternative to MTX treatment in terms of treatment success, future pregnancy, health related quality of life and costs.
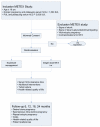
Methods/design: A multicentre randomised controlled trial in The Netherlands. Hemodynamically stable patients with an EP visible on transvaginal ultrasound and a plateauing serum hCG concentration < 1,500 IU/L or with a persisting PUL with plateauing serum hCG concentrations < 2,000 IU/L are eligible for the trial. Patients with a viable EP, signs of tubal rupture/abdominal bleeding, or a contra-indication for MTX will not be included. Expectant management is compared with systemic MTX in a single dose intramuscular regimen (1 mg/kg) in an outpatient setting. Serum hCG levels are monitored weekly; in case of inadequately declining, systemic MTX is installed or continued. In case of hemodynamic instability and/or signs of tubal rupture, surgery is performed. The primary outcome measure is an uneventful decline of serum hCG to an undetectable level by the initial intervention. Secondary outcomes are (re)interventions (additional systemic MTX injections and/or surgery), treatment complications, health related quality of life, financial costs, and future fertility. Analysis is performed according to the intention to treat principle. Quality of life is assessed by questionnaires before and at three time points after randomisation. Costs are expressed as direct costs with data on costs and used resources in the participating centres. Fertility is assessed by questionnaires after 6, 12, 18 and 24 months. Patients' preferences will be assessed using a discrete choice experiment.
Discussion: This trial will provide guidance on the present management dilemmas in women with EPs and PULs with low and plateauing serum hCG concentrations.
Trial registration: Current Controlled Trials ISRCTN 48210491.
References
-
- Centre for disease Control Ectopic pregnancy surveillance in the United States 1970–87. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1990;39:401–3. - PubMed
-
- Why mothers die. Report on Confidential Enquiries into Maternal Deaths in the United Kingdom 1994–1996. HMSO, London; 1998. - PubMed
-
- National Medical Register of the Organization for Dutch Health Care Information. Utrecht, The Netherlands; 1992.
-
- Storeide O, Veholmen M, Elde M, Bergsjo P, Sandvel R. The incidence of ectopic pregnancy in Hordaland county, Norway 1976–93. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1997;76:345–9. - PubMed
-
- Ankum WM, Veen F van der, Hamerlynck JVThH, Lammes FB. Laparoscopy: a dispensable tool in the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy? Hum Reprod. 1993;8:1301–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical