ERP measures of partial semantic knowledge: left temporal indices of skill differences and lexical quality
- PMID: 18565637
- PMCID: PMC3293183
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2008.04.017
ERP measures of partial semantic knowledge: left temporal indices of skill differences and lexical quality
Abstract
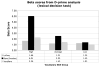
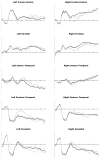
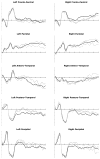
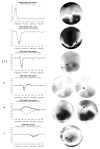
This study examines the sensitivity of early event-related potentials (ERPs) to degrees of word semantic knowledge. Participants with strong, average, or weak vocabulary skills made speeded lexical decisions to letter strings. To represent the full spectrum of word knowledge among adult native-English speakers, we used rare words that were orthographically matched with more familiar words and with pseudowords. Since the lexical decision could not reliably be made on the basis of word form, subjects were obliged to use semantic knowledge to perform the task. A d' analysis suggested that high-skilled subjects adopted a more conservative strategy in response to rare versus more familiar words. Moreover, the high-skilled participants showed a trend towards an enhanced "N2c" to rare words, and a similar posterior temporal effect reached significance approximately 650 ms. Generators for these effects were localized to left temporal cortex. We discuss implications of these results for word learning and for theories of lexical semantic access.
Figures





References
-
- Beck I, McKeown M, Kucan L. Bringing Words to Life: Robust Vocabulary Instruction. Guilford Press; New York: 2002.
-
- Bentin S, Mouchetant-Rostaing Y, Giard MH, Echallier JF, Pernier J. ERP manifestations of processing printed words at different psycholinguistic levels: time course and scalp distribution. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 1999;11 (3):235–260. - PubMed
-
- Binder JR, McKiernan KA, Parsons ME, Westbury CF, Possing ET, Kaufman JN, et al. Neural correlates of lexical access during visual word recognition. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2003;15 (3):372–393. - PubMed
-
- Brown JI, Fishko VV, Hanna G. Nelson–Denny Reading Test. Riverside Publishing Co; New York: 1993.
-
- Brown J, Frishkoff G, Eskenazi M. Automatic question generation for vocabulary assessment. Proceedings of the Annual Human Language Technology Meeting; October 6–8; Vancouver, BC. 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

