Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma regulates the expression of alveolar macrophage macrophage colony-stimulating factor
- PMID: 18566389
- PMCID: PMC2819287
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.1.235
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma regulates the expression of alveolar macrophage macrophage colony-stimulating factor
Abstract
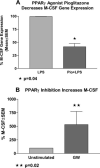
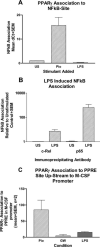
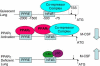
Macrophage CSF (M-CSF) regulates monocyte differentiation, activation, and foam cell formation. We have observed that it is elevated in human pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) and in the GM-CSF knockout mouse, a murine model for PAP. A potential regulator of M-CSF, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma), is severely deficient in both human PAP and the GM-CSF knockout mouse. To investigate the role of PPARgamma in alveolar macrophage homeostasis, we generated myeloid-specific PPARgamma knockout mice using the Lys-Cre method to knock out the floxed PPARgamma gene. Similar to the GM-CSF-deficient mouse, absence of alveolar macrophage PPARgamma resulted in development of lung pathology resembling PAP in 16-wk-old mice, along with excess M-CSF gene expression and secretion. In ex vivo wild-type alveolar macrophages, we observed that M-CSF itself is capable of inducing foam cell formation similar to that seen in PAP. Overexpression of PPARgamma prevented LPS-stimulated M-CSF production in RAW 264.7 cells, an effect that was abrogated by a specific PPARgamma antagonist, GW9662. Use of proteasome inhibitor, MG-132 or a PPARgamma agonist, pioglitazone, prevented LPS-mediated M-CSF induction. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation, we found that PPARgamma is capable of regulating M-CSF through transrepression of NF-kappaB binding at the promoter. Gel-shift assay experiments confirmed that pioglitazone is capable of blocking NF-kappaB binding. Taken together, these data suggest that M-CSF is an important mediator of alveolar macrophage homeostasis, and that transcriptional control of M-CSF production is regulated by NF-kappaB and PPARgamma.
Figures




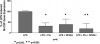

References
-
- Berger J, Moller DE. The mechanisms of action of PPARs. Annu. Rev. Med. 2002;53:409–435. - PubMed
-
- Clark RB. The role of PPARs in inflammation and immunity. J. Leukocyte Biol. 2002;71:388–400. - PubMed
-
- Chinetti G, Griglio S, Antonucci M, Torra IP, Delerive P, Majd Z, Fruchart J-C, Chapman J, Najib J, Staels B. Activation of proliferator-activated receptors alpha and gamma induces apoptosis of human monocyte-derived macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:25573–25580. - PubMed
-
- Bonfield TL, Russell D, Burgess S, Malur A, Kavuru MS, Thomassen MJ. Autoantibodies against granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor are diagnostic for pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2002;27:481–486. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

