CD73 participates in cellular multiresistance program and protects against TRAIL-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 18566412
- PMCID: PMC5584620
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.1.464
CD73 participates in cellular multiresistance program and protects against TRAIL-induced apoptosis
Abstract
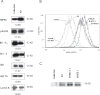
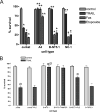
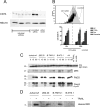
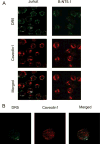
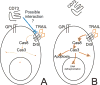
The molecular mechanisms underlying the multiresistant phenotype of leukemic and other cancer cells are incompletely understood. We used expression arrays to reveal differences in the gene expression profiles of an apoptosis-resistant T cell leukemia clone (A4) and normally apoptosis-sensitive parental Jurkat cells. CD73 (ecto-5'-nucleotidase) was the most up-regulated gene in the resistant A4 cell clone. A4 cells displayed CD73 surface expression and significant ecto-5'-nucleotidase activity. The role of CD73 was confirmed by transfection of wild-type CD73 into native Jurkat cells, which led to specific resistance against TRAIL-induced apoptosis, but not other types of apoptosis. The protective role of CD73 was further confirmed by small interfering RNA-mediated down-regulation of CD73, restoring TRAIL sensitivity. CD73-mediated resistance was independent of enzymatic activity of CD73, but was reliant on the anchoring of the protein to the membrane via GPI. We suggest that the inhibition of TRAIL signaling works through interaction of CD73 with death receptor 5, as CD73 and death receptor 5 could be coimmunoprecipitated and were shown to be colocalized in the plasma membrane by confocal microscopy. We propose that CD73 is a component of multiresistance machinery, the transcription of which is activated under selective pressure of the immune system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Upregulation of CD73 Confers Acquired Radioresistance and is Required for Maintaining Irradiation-selected Pancreatic Cancer Cells in a Mesenchymal State.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020 Feb;19(2):375-389. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001779. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 31879272 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Ecto-5'-nucleotidase (CD73) promotes T-47D human breast cancer cells invasion and adhesion to extracellular matrix.Cancer Biol Ther. 2007 Mar;6(3):426-31. doi: 10.4161/cbt.6.3.3762. Epub 2007 Mar 29. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17471030
-
Ecto-enzyme and signaling functions of lymphocyte CD73.Immunol Rev. 1998 Feb;161:95-109. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1998.tb01574.x. Immunol Rev. 1998. PMID: 9553767 Review.
-
Ecto-5'-nucleotidase/CD73 knockdown increases cell migration and mRNA level of collagen I in a hepatic stellate cell line.Cell Tissue Res. 2011 May;344(2):279-86. doi: 10.1007/s00441-011-1140-7. Epub 2011 Mar 19. Cell Tissue Res. 2011. PMID: 21424267
-
CD73 (ecto-5'-nucleotidase) on blood mononuclear cells. Regulation of ecto-5'-nucleotidase activity and antigenic heterogeneity of CD73 on blood mononuclear cells from healthy donors and from patients with immunodeficiency.APMIS Suppl. 1997;73:1-28. APMIS Suppl. 1997. PMID: 9393563 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
CD73 Promotes Age-Dependent Accretion of Atherosclerosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Jan;40(1):61-71. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.313002. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 31619062 Free PMC article.
-
Graft-versus-host disease is enhanced by selective CD73 blockade in mice.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58397. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058397. Epub 2013 Mar 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23520507 Free PMC article.
-
CD73 Downregulation Decreases In Vitro and In Vivo Glioblastoma Growth.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 May;56(5):3260-3279. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1240-4. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30117104
-
Cell type- and tissue-specific functions of ecto-5'-nucleotidase (CD73).Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Dec 1;317(6):C1079-C1092. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00285.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31461341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in the Surface Expression of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 3, the Induction of Apoptosis, and the Inhibition of Cell-Cycle Progression of Human Multidrug-Resistant Jurkat/A4 Cells Exposed to a Random Positioning Machine.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 28;21(3):855. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030855. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32013031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ng C, Bonavida B. A new challenge for successful immunotherapy by tumors that are resistant to apoptosis: two complementary signals to overcome cross-resistance. Adv Cancer Res. 2002;85:145–174. - PubMed
-
- Piche A, Rancourt C. Gene therapy to overcome drug resistance in cancer: targeting key regulators of the apoptotic pathway. Curr Gene Ther. 2001;1:317–324. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson K, Anderson N. The protein kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy. Cell Signal. 2002;14:381–395. - PubMed
-
- Stambolic V, Mak T, Woodgett J. Modulation of cellular apoptotic potential: contributions to oncogenesis. Oncogene. 1999;18:6094–6103. - PubMed
-
- Leong K, Karsan A. Signaling pathways mediated by tumor necrosis factor α. Histol Histopathol. 2000;15:1303–1325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

