Lipoperoxidation and protein oxidative damage exhibit different kinetics during septic shock
- PMID: 18566692
- PMCID: PMC2430274
- DOI: 10.1155/2008/168652
Lipoperoxidation and protein oxidative damage exhibit different kinetics during septic shock
Abstract
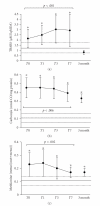
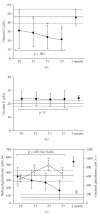
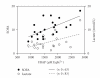
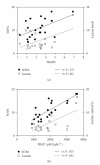
Septic shock (SS)-related multiorgan dysfunction has been associated with oxidative damage, but little is known about the temporal damage profile and its relationship to severity. The present work investigated prospectively 21 SS patients. Blood samples were obtained at diagnosis, 24, 72 hours, day 7, and at 3 months. At admission, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARSs), plasma protein carbonyls, plasma protein methionine sulfoxide (MS), ferric/reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), total red blood cell glutathione (RBCG), uric acid (UA), and bilirrubin levels were increased (P < .05). Total radical-trapping antioxidant potential (TRAP) and vitamin-E were similar to controls, and vitamin-C was decreased (P < .05). During evolution, TBARS and RBCG increased (P < .001), vitamin-E levels remained stable, whereas plasma protein carbonyls and MS, TRAP, vitamin-C, reduced glutathione, and UA levels decreased (P < .006). After 3 months, plasma protein carbonyls and MS persisted elevated. More severe patients exhibited higher TBARS, TRAP, FRAP, vitamin-C, UA, and bilirrubin levels. Our results suggest early and persistent oxidative stress during septic shock and a correlation between increasing levels of lipoperoxidation and sepsis severity.
Figures

References
-
- Weiss U. Inflammation. Nature. 2002;420(6917):p. 845.
-
- Galley HF, Davies MJ, Webster NR. Xanthine oxidase activity and free radical generation in patients with sepsis syndrome. Critical Care Medicine. 1996;24(10):1649–1653. - PubMed
-
- Victor VM, Rocha M, De la Fuente M. Immune cells: free radicals and antioxidants in sepsis. International Immunopharmacology. 2004;4(3):327–347. - PubMed
-
- Galley HF, Howdle PD, Walker BE, Webster NR. The effects of intravenous antioxidants in patients with septic shock. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 1997;23(5):768–774. - PubMed
-
- Winterbourn CC, Buss IH, Chan TP, Plank LD, Clark MA, Windsor JA. Protein carbonyl measurements show evidence of early oxidative stress in critically ill patients. Critical Care Medicine. 2000;28(1):143–149. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

