Influence of dexamethasone on mesenteric lymph node of rats with severe acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 18567079
- PMCID: PMC2716613
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.3511
Influence of dexamethasone on mesenteric lymph node of rats with severe acute pancreatitis
Abstract
Aim: To study the influence and mechanisms of dexamethasone on mesenteric lymph node of rats with severe acute pancreatitis (SAP).
Methods: The SAP rats were assigned to model, treated or sham-operated groups. The mortality, pathological changes of mesenteric lymph nodes, expression levels of NF-kappa B, P-selectin, Bax, Bcl-2 and caspase-3 protein and changes in apoptotic indexes in lymph nodes were observed at 3, 6 and 12 h after operation. The blood levels of endotoxin, superoxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA), and endothelin-1 (ET-1) in blood were determined.
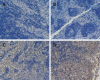
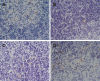
Results: SOD content, expression of Bax protein and apoptotic index were significantly higher in the treated group than in the model group at different time points (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). Other blood-detecting indexes and histopathological scores of mesenteric lymph nodes were lower in the treated than in the model group (P < 0.05, P < 0.01 or P < 0.01). NF-kappa B protein expression was negative in all groups. Comparing P-selectin and caspase-3 expression levels among all three groups, there was no marked difference between the model and treated group.
Conclusion: Dexamethasone can protect mesenteric lymph nodes. The mechanism may be by reducing the content of inflammatory mediators in the blood and inducing lymphocyte apoptosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Baicalin protects thymus of rats with severe acute pancreatitis.Inflammation. 2010 Jun;33(3):157-65. doi: 10.1007/s10753-009-9169-4. Inflammation. 2010. PMID: 19953313
-
Protecting effects of a large dose of dexamethasone on spleen injury of rats with severe acute pancreatitis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Feb;25(2):302-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.05999.x. Epub 2009 Oct 27. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 19874442
-
Study of dexamethasone, baicalin and octreotide on brain injury of rats with severe acute pancreatitis.Inflamm Res. 2012 Mar;61(3):265-75. doi: 10.1007/s00011-011-0408-4. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Inflamm Res. 2012. PMID: 22166920
-
Study of the protective effects of dexamethasone on ileum mucosa injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis.Pancreas. 2008 Oct;37(3):e74-82. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181800d11. Pancreas. 2008. PMID: 18815542
-
Assessment of the morphology and significance of the lymph nodal and hepatic lesions produced in rats by the feeding of certain mineral oils and waxes. Proceedings of a pathology workshop held at the Fraunhofer Institute of Toxicology and Aerosol Research Hannover, Germany, May 7-9, 2001.Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2001 Sep;53(4):247-55. doi: 10.1078/0940-2993-00198. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11665848 Review.
Cited by
-
Free Total Rhubarb Anthraquinones Protect Intestinal Injury via Regulation of the Intestinal Immune Response in a Rat Model of Severe Acute Pancreatitis.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Feb 13;9:75. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00075. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29487524 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhizae injection in the treatment of rats with severe acute pancreatitis.Inflammation. 2009 Apr;32(2):109-19. doi: 10.1007/s10753-009-9109-3. Inflammation. 2009. PMID: 19238530
-
Breviscapine attenuates acute pancreatitis by inhibiting expression of PKCα and NF-κB in pancreas.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Apr 14;17(14):1825-30. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i14.1825. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21528054 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Salvia miltiorrhizae on the mesenteric lymph node of rats with severe acute pancreatitis or obstructive jaundice.Mediators Inflamm. 2009;2009:675195. doi: 10.1155/2009/675195. Epub 2010 Feb 15. Mediators Inflamm. 2009. PMID: 20169004 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of dexamethasone on the expression levels of P-selectin protein in multiple organs of rats with severe acute pancreatitis.Inflamm Res. 2010 Jan;59(1):31-9. doi: 10.1007/s00011-009-0067-x. Epub 2009 Aug 5. Inflamm Res. 2010. PMID: 19655231
References
-
- Zhang XP, Zhang L, Xu HM, Xu YP, Cheng QH, Wang JM, Shen HP. Application of tissue microarrays to study the influence of dexamethasone on NF-kappaB expression of pancreas in rat with severe acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53:571–580. - PubMed
-
- Zhang XP, Zhang L, Wang Y, Cheng QH, Wang JM, Cai W, Shen HP, Cai J. Study of the protective effects of dexamethasone on multiple organ injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. JOP. 2007;8:400–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

