Ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 mediates tumor necrosis factor-induced systemic bone loss by promoting proteasomal degradation of bone morphogenetic signaling proteins
- PMID: 18567580
- PMCID: PMC2517001
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M709848200
Ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 mediates tumor necrosis factor-induced systemic bone loss by promoting proteasomal degradation of bone morphogenetic signaling proteins
Abstract
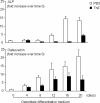
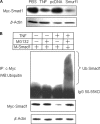
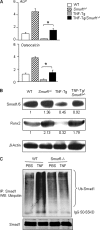
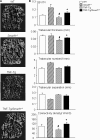
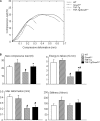
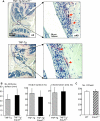
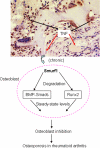
Chronic inflammatory disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, are often accompanied by systemic bone loss, which is thought to occur through inflammatory cytokine-mediated stimulation of osteoclast resorption and inhibition of osteoblast function. However, the mechanisms involved in osteoblast inhibition remain poorly understood. Here we test the hypothesis that increased Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor 1 (Smurf1)-mediated degradation of the bone morphogenetic protein pathway signaling proteins mediates reduced bone formation in inflammatory disorders. Osteoblasts derived from bone marrow or long bone samples of adult tumor necrosis factor (TNF) transgenic (TNF-Tg) mice were used in this study. TNF decreased the steady-state levels of Smad1 and Runx2 protein similarly to those in long bones of TNF-Tg mice. In the presence of the proteasome inhibitor MG132, TNF increased accumulation of ubiquitinated Smad1 protein. TNF administration over calvarial bones caused decreases in Smad1 and Runx2 protein levels and mRNA expression of osteoblast marker genes in wild-type, but not in Smurf1(-/-) mice. Vertebral bone volume and strength of TNF-Tg/Smurf1(-/-) mice were examined by a combination of micro-CT, bone histomorphometry, and biomechanical testing and compared with those from TNF-Tg littermates. TNF-Tg mice had significantly decreased bone volume and biomechanical properties, which were partially rescued in TNF-Tg/Smurf1(-/-) mice. We conclude that in chronic inflammatory disorders where TNF is increased, TNF induces the expression of ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 and promotes ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of Smad1 and Runx2, leading to systemic bone loss. Inhibition of ubiquitin-mediated Smad1 and Runx2 degradation in osteoblasts could help to treat inflammation-induced osteoporosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor promotes Runx2 degradation through up-regulation of Smurf1 and Smurf2 in osteoblasts.J Biol Chem. 2006 Feb 17;281(7):4326-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509430200. Epub 2005 Dec 22. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16373342 Free PMC article.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 mediates core-binding factor alpha1/Runx2 degradation and plays a specific role in osteoblast differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jul 25;278(30):27939-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304132200. Epub 2003 May 7. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12738770
-
Smad6 interacts with Runx2 and mediates Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor 1-induced Runx2 degradation.J Biol Chem. 2006 Feb 10;281(6):3569-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506761200. Epub 2005 Nov 18. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16299379 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β inhibits osteogenesis by upregulating the expression of ubiquitin ligase SMURF1 via MAPK-ERK signaling.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jan;233(1):596-606. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25920. Epub 2017 Jun 5. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28322449
-
Regulatory Roles of E3 Ubiquitin Ligases and Deubiquitinases in Bone.Biomolecules. 2025 May 7;15(5):679. doi: 10.3390/biom15050679. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40427572 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Neddylation Suppresses Osteoclast Differentiation and Function In Vitro and Alleviates Osteoporosis In Vivo.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 21;10(10):2355. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102355. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289618 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of bone fragility in a mouse model of glucocorticoid-treated rheumatoid arthritis: implications for insufficiency fracture risk.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Nov;64(11):3649-59. doi: 10.1002/art.34639. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22832945 Free PMC article.
-
[New from old : relevant factors for fracture healing in aging bone].Orthopade. 2014 Apr;43(4):298-305. doi: 10.1007/s00132-013-2160-7. Orthopade. 2014. PMID: 24671345 Review. German.
-
Tumor necrosis factor inhibits mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into osteoblasts via the ubiquitin E3 ligase Wwp1.Stem Cells. 2011 Oct;29(10):1601-10. doi: 10.1002/stem.703. Stem Cells. 2011. PMID: 21809421 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin E3 ligase Itch negatively regulates osteoblast function by promoting proteasome degradation of osteogenic proteins.Bone Joint Res. 2017 Mar;6(3):154-161. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.63.BJR-2016-0237.R1. Bone Joint Res. 2017. PMID: 28298321 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

