Locally produced C5a binds to T cell-expressed C5aR to enhance effector T-cell expansion by limiting antigen-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 18567839
- PMCID: PMC2518884
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-04-151068
Locally produced C5a binds to T cell-expressed C5aR to enhance effector T-cell expansion by limiting antigen-induced apoptosis
Abstract
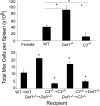
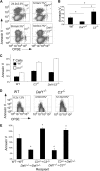
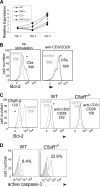
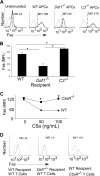
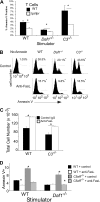
Our recent studies have shown that immune cell-produced complement provides costimulatory and survival signals to naive CD4(+) T cells. Whether these signals are similarly required during effector cell expansion and what molecular pathways link locally produced complement to T-cell survival were not clarified. To address this, we stimulated monoclonal and polyclonal T cells in vitro and in vivo with antigen-presenting cells (APCs) deficient in the complement regulatory protein, decay accelerating factor (DAF), and/or the complement component C3. We found that T-cell expansion induced by DAF-deficient APCs was augmented with diminished T-cell apoptosis, whereas T-cell expansion induced by C3(-/-) APCs was reduced because of enhanced T-cell apoptosis. These effects were traced to locally produced C5a, which through binding to T cell-expressed C5aR, enhanced expression of Bcl-2 and prevented Fas up-regulation. The results show that C5aR signal transduction in T cells is important to allow optimal T-cell expansion, as well as to maintain naive cell viability, and does so by suppressing programmed cell death.
Figures


Comment in
-
Complement dances with T cells.Blood. 2008 Sep 1;112(5):1551-2. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-07-168179. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18725570 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hildeman DA, Zhu Y, Mitchell TC, et al. Activated T cell death in vivo mediated by proapoptotic bcl-2 family member bim. Immunity. 2002;16:759–767. - PubMed
-
- Ju ST, Panka DJ, Cui H, et al. Fas(CD95)/FasL interactions required for programmed cell death after T-cell activation. Nature. 1995;373:444–448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

