Pungent agents from Szechuan peppers excite sensory neurons by inhibiting two-pore potassium channels
- PMID: 18568022
- PMCID: PMC3072296
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2143
Pungent agents from Szechuan peppers excite sensory neurons by inhibiting two-pore potassium channels
Abstract
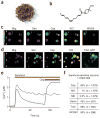
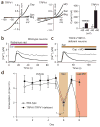
In traditional folk medicine, Xanthoxylum plants are referred to as 'toothache trees' because their anesthetic or counter-irritant properties render them useful in the treatment of pain. Psychophysical studies have identified hydroxy-alpha-sanshool as the compound most responsible for the unique tingling and buzzing sensations produced by Szechuan peppercorns or other Xanthoxylum preparations. Although it is generally agreed that sanshool elicits its effects by activating somatosensory neurons, the underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms remain a matter of debate. Here we show that hydroxy-alpha-sanshool excites two types of sensory neurons, including small-diameter unmyelinated cells that respond to capsaicin (but not mustard oil) as well as large-diameter myelinated neurons that express the neurotrophin receptor TrkC. We found that hydroxy-alpha-sanshool excites neurons through a unique mechanism involving inhibition of pH- and anesthetic-sensitive two-pore potassium channels (KCNK3, KCNK9 and KCNK18), providing a framework for understanding the unique and complex psychophysical sensations associated with the Szechuan pepper experience.
Figures
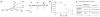
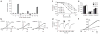
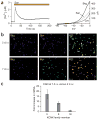
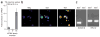
References
-
- Meyer RA, Ringkamp M, Campbell JN, Raja SN. Peripheral mechanisms of cutaneous nociception. In: McMahon SB, Koltzenburg M, editors. Textbook of Pain. Elsevier; Philadelphia: 2006. pp. 3–34.
-
- Julius D, Basbaum AI. Molecular mechanisms of nociception. Nature. 2001;413:203–210. - PubMed
-
- Fields HL. Pain. McGraw-Hill; New York: 1987.
-
- Snyder SH. Opiate receptors and internal opiates. Sci Am. 1977;236:44–56. - PubMed
-
- Julius D. From peppers to peppermints: natural products as probes of the pain pathway. Harvey Lect. 2005;101:89–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

