Electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry: principles and clinical applications
- PMID: 18568044
- PMCID: PMC1853331
Electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry: principles and clinical applications
Abstract
This mini-review provides a general understanding of electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) which has become an increasingly important technique in the clinical laboratory for structural study or quantitative measurement of metabolites in a complex biological sample. The first part of the review explains the electrospray ionisation process, design of mass spectrometers with separation capability, characteristics of the mass spectrum, and practical considerations in quantitative analysis. The second part then focuses on some clinical applications. The capability of ESI-tandem-MS in measuring bio-molecules sharing similar molecular structures makes it particularly useful in screening for inborn errors of amino acid, fatty acid, purine, pyrimidine metabolism and diagnosis of galactosaemia and peroxisomal disorders. Electrospray ionisation is also efficient in generating cluster ions for structural elucidation of macromolecules. This has fostered a new and improved approach (vs electrophoresis) for identification and quantification of haemoglobin variants. With the understanding of glycohaemoglobin structure, an IFCC reference method for glycohaemoglobin assay has been established using ESI-MS. It represents a significant advancement for the standardisation of HbA1c in diabetic monitoring. With its other applications such as in therapeutic drug monitoring, ESI-MS will continue to exert an important influence in the future development and organisation of the clinical laboratory service.
Figures

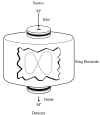

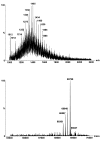

Similar articles
-
Recent studies on the electrospray ionisation mass spectrometric behaviour of selected nitrogen-containing drug molecules and its application to drug analysis using liquid chromatography-electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2005 Sep 25;824(1-2):1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2005.07.018. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 16095984 Review.
-
The potential of organic (electrospray- and atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation) mass spectrometric techniques coupled to liquid-phase separation for speciation analysis.J Chromatogr A. 2003 Jun 6;1000(1-2):841-89. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(03)00603-4. J Chromatogr A. 2003. PMID: 12877203 Review.
-
ESI-MS/MS analysis of underivatised amino acids: a new tool for the diagnosis of inherited disorders of amino acid metabolism. Fragmentation study of 79 molecules of biological interest in positive and negative ionisation mode.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2003;17(12):1297-1311. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1054. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2003. PMID: 12811753
-
A critical evaluation of high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionisation-mass spectrometry and capillary electrophoresis-electrospray-mass spectrometry for the detection and determination of small molecules of significance in clinical and forensic science.Electrophoresis. 2004 Jun;25(10-11):1413-46. doi: 10.1002/elps.200305850. Electrophoresis. 2004. PMID: 15188226 Review.
-
The characterisation of selected antidepressant drugs using electrospray ionisation with ion trap mass spectrometry and with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and their determination by high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2006;20(11):1637-42. doi: 10.1002/rcm.2485. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2006. PMID: 16636998
Cited by
-
Selenium-enriched plant foods: Selenium accumulation, speciation, and health functionality.Front Nutr. 2023 Feb 6;9:962312. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.962312. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36815133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Observation and identification of autofluorescent urine crystals may be linked to a sign of urolithiasis.Urolithiasis. 2022 Oct;50(5):535-543. doi: 10.1007/s00240-022-01343-0. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Urolithiasis. 2022. PMID: 35876891
-
Standardization via Post Column Infusion-A Novel and Convenient Quantification Approach for LC-MS/MS.Molecules. 2024 Aug 12;29(16):3829. doi: 10.3390/molecules29163829. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39202908 Free PMC article.
-
Quasi-continuous infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization source coupled to a quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer for direct analysis from well plates.J Mass Spectrom. 2023 Jan;58(1):e4902. doi: 10.1002/jms.4902. J Mass Spectrom. 2023. PMID: 36694312 Free PMC article.
-
Present and Future Applications of High Resolution Mass Spectrometry in the Clinic.Discoveries (Craiova). 2014 Jun 30;2(2):e17. doi: 10.15190/d.2014.9. Discoveries (Craiova). 2014. PMID: 32309546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruins AP. Mechanistic aspects of electrospray ionization. J Chromatogr A. 1998;794:345–57.
-
- Rashed MS, Ozand PT, Bucknall MP, Little D. Diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism from blood spots by acylcarnitines and amino acids profiling using automated electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Pediatr Res. 1995;38:324–31. - PubMed
-
- Jardine I. Molecular weight analysis of proteins. In: McCloskey JA, editor. Methods in Enzymology, Volume 193, pp 441–55. Pasadena: Academic Press, 1990. - PubMed
-
- Stevens RD, Hillman SL, Worthy S, Sanders D, Millington DS. Assay for free and total carnitine in human plasma using tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 2000;46:727–9. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Q, Simpson J, Aboleneen HI. A specific method for the measurement of tacrolimus in human whole blood by liquid chromatography / tandem mass spectrometry. Thera Drug Monit. 1997;19:470–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
